Development of personalized tumor biomarkers using massively parallel sequencing
- PMID: 20371490
- PMCID: PMC2858564
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3000702
Development of personalized tumor biomarkers using massively parallel sequencing
Abstract
Clinical management of human cancer is dependent on the accurate monitoring of residual and recurrent tumors. The evaluation of patient-specific translocations in leukemias and lymphomas has revolutionized diagnostics for these diseases. We have developed a method, called personalized analysis of rearranged ends (PARE), which can identify translocations in solid tumors. Analysis of four colorectal and two breast cancers with massively parallel sequencing revealed an average of nine rearranged sequences (range, 4 to 15) per tumor. Polymerase chain reaction with primers spanning the breakpoints was able to detect mutant DNA molecules present at levels lower than 0.001% and readily identified mutated circulating DNA in patient plasma samples. This approach provides an exquisitely sensitive and broadly applicable approach for the development of personalized biomarkers to enhance the clinical management of cancer patients.
Figures
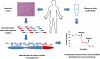


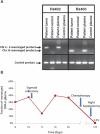
Comment in
-
Cancer sequencing gets a little more personal.Sci Transl Med. 2010 Feb 24;2(20):20ps8. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3000929. Sci Transl Med. 2010. PMID: 20371489
References
-
- Lengauer C, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. Genetic instabilities in human cancers. Nature. 1998;396:643–649. - PubMed
-
- Mitelman F, Johansson B, Mertens F. The impact of translocations and gene fusions on cancer causation. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2007;7:233–245. - PubMed
-
- Pinkel D, Segraves R, Sudar D, Clark S, Poole I, Kowbel D, Collins C, Kuo WL, Chen C, Zhai Y, Dairkee SH, Ljung BM, Gray JW, Albertson DG. High resolution analysis of DNA copy number variation using comparative genomic hybridization to microarrays. Nat. Genet. 1998;20:207–211. - PubMed
-
- Lucito R, Healy J, Alexander J, Reiner A, Esposito D, Chi M, Rodgers L, Brady A, Sebat J, Troge J, West JA, Rostan S, Nguyen KC, Powers S, Ye KQ, Olshen A, Venkatraman E, Norton L, Wigler M. Representational oligonucleotide microarray analysis: A high-resolution method to detect genome copy number variation. Genome Res. 2003;13:2291–2305. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

