CdnL, a member of the large CarD-like family of bacterial proteins, is vital for Myxococcus xanthus and differs functionally from the global transcriptional regulator CarD
- PMID: 20371514
- PMCID: PMC2919716
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq214
CdnL, a member of the large CarD-like family of bacterial proteins, is vital for Myxococcus xanthus and differs functionally from the global transcriptional regulator CarD
Abstract
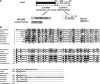
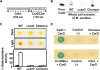
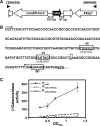
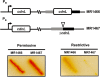
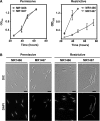
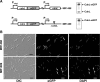
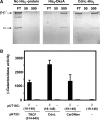
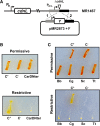
CarD, a global transcriptional regulator in Myxococcus xanthus, interacts with CarG via CarDNter, its N-terminal domain, and with DNA via a eukaryotic HMGA-type C-terminal domain. Genomic analysis reveals a large number of standalone proteins resembling CarDNter. These constitute, together with the RNA polymerase (RNAP) interacting domain, RID, of transcription-repair coupling factors, the CarD_TRCF protein family. We show that one such CarDNter-like protein, M. xanthus CdnL, cannot functionally substitute CarDNter (or vice versa) nor interact with CarG. Unlike CarD, CdnL is vital for growth, and lethality due to its absence is not rescued by homologs from various other bacteria. In mycobacteria, with no endogenous DksA, the function of the CdnL homolog mirrors that of Escherichia coli DksA. Our finding that CdnL, like DksA, is indispensable in M. xanthus implies that they are not functionally redundant. Cells are normal on CdnL overexpression, but divide aberrantly on CdnL depletion. CdnL localizes to the nucleoid, suggesting piggyback recruitment by factors such as RNAP, which we show interacts with CdnL, CarDNter and RID. Our study highlights a complex network of interactions involving these factors and RNAP, and points to a vital role for M. xanthus CdnL in an essential DNA transaction that affects cell division.
Figures
Similar articles
-
House of CarDs: Functional insights into the transcriptional regulator CdnL.Mol Microbiol. 2024 Nov;122(5):789-796. doi: 10.1111/mmi.15268. Epub 2024 Apr 25. Mol Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38664995 Review.
-
Structure-function dissection of Myxococcus xanthus CarD N-terminal domain, a defining member of the CarD_CdnL_TRCF family of RNA polymerase interacting proteins.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 26;10(3):e0121322. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121322. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25811865 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into RNA polymerase recognition and essential function of Myxococcus xanthus CdnL.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 1;9(10):e108946. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108946. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25272012 Free PMC article.
-
High-mobility-group a-like CarD binds to a DNA site optimized for affinity and position and to RNA polymerase to regulate a light-inducible promoter in Myxococcus xanthus.J Bacteriol. 2013 Jan;195(2):378-88. doi: 10.1128/JB.01766-12. Epub 2012 Nov 9. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23144251 Free PMC article.
-
The regulatory action of the myxobacterial CarD/CarG complex: a bacterial enhanceosome?FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2010 Sep;34(5):764-78. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2010.00235.x. Epub 2010 May 20. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20561058 Review.
Cited by
-
House of CarDs: Functional insights into the transcriptional regulator CdnL.Mol Microbiol. 2024 Nov;122(5):789-796. doi: 10.1111/mmi.15268. Epub 2024 Apr 25. Mol Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38664995 Review.
-
Ribosome engineering of Myxococcus xanthus for enhancing the heterologous production of epothilones.Microb Cell Fact. 2024 Dec 27;23(1):346. doi: 10.1186/s12934-024-02627-3. Microb Cell Fact. 2024. PMID: 39725983 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for the bacterial transcription-repair coupling factor/RNA polymerase interaction.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Dec;38(22):8357-69. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq692. Epub 2010 Aug 11. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20702425 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the transcription factor CdnL promotes adaptation to nutrient stress in Caulobacter.PNAS Nexus. 2024 Apr 10;3(4):pgae154. doi: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgae154. eCollection 2024 Apr. PNAS Nexus. 2024. PMID: 38650860 Free PMC article.
-
Mfd Protein and Transcription-Repair Coupling in Escherichia coli.Photochem Photobiol. 2017 Jan;93(1):280-295. doi: 10.1111/php.12675. Epub 2017 Jan 18. Photochem Photobiol. 2017. PMID: 27864884 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dawid W. Biology and global distribution of myxobacteria in soils. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2000;24:403–427. - PubMed
-
- Kaiser D. Signaling in myxobacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2004;58:75–98. - PubMed
-
- Zusman DR, Scott AE, Yang Z, Kirby JR. Chemosensory pathways, motility and development in Myxococcus xanthus. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007;5:862–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

