Rad52 SUMOylation affects the efficiency of the DNA repair
- PMID: 20371517
- PMCID: PMC2919706
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq195
Rad52 SUMOylation affects the efficiency of the DNA repair
Erratum in
- Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Apr;40(8):3775
-
Correction to 'Rad52 SUMOylation affects the efficiency of the DNA repair'.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Feb 28;51(4):1998. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad065. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36715321 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Homologous recombination (HR) plays a vital role in DNA metabolic processes including meiosis, DNA repair, DNA replication and rDNA homeostasis. HR defects can lead to pathological outcomes, including genetic diseases and cancer. Recent studies suggest that the post-translational modification by the small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) protein plays an important role in mitotic and meiotic recombination. However, the precise role of SUMOylation during recombination is still unclear. Here, we characterize the effect of SUMOylation on the biochemical properties of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae recombination mediator protein Rad52. Interestingly, Rad52 SUMOylation is enhanced by single-stranded DNA, and we show that SUMOylation of Rad52 also inhibits its DNA binding and annealing activities. The biochemical effects of SUMO modification in vitro are accompanied by a shorter duration of spontaneous Rad52 foci in vivo and a shift in spontaneous mitotic recombination from single-strand annealing to gene conversion events in the SUMO-deficient Rad52 mutants. Taken together, our results highlight the importance of Rad52 SUMOylation as part of a 'quality control' mechanism regulating the efficiency of recombination and DNA repair.
Figures


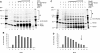
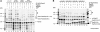
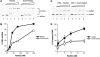


References
-
- Krogh BO, Symington LS. Recombination proteins in yeast. Ann. Rev. Genet. 2004;38:233–271. - PubMed
-
- Sung P, Klein H. Mechanism of homologous recombination: mediators and helicases take on regulatory functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006;7:739–750. - PubMed
-
- Sung P. Function of yeast Rad52 protein as a mediator between replication protein A and the Rad51 recombinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:28194–28197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

