A new fractionation assay, based on the size of formaldehyde-crosslinked, mildly sheared chromatin, delineates the chromatin structure at promoter regions
- PMID: 20371521
- PMCID: PMC2887976
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq203
A new fractionation assay, based on the size of formaldehyde-crosslinked, mildly sheared chromatin, delineates the chromatin structure at promoter regions
Abstract
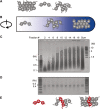
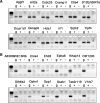
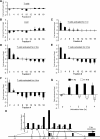
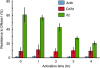
To explore the higher order structure of transcribable chromatin in vivo, its local configuration was assessed through the accessibility of the chromatin to crosslinking with formaldehyde. The application of crosslinked and mildly sheared chromatin to sedimentation velocity centrifugation followed by size-fractionation of the DNA enabled us to biochemically distinguish between chromatin with heavily versus sparsely crosslinkable structures. The separated fractions showed a good correlation with gene expression profiles. Genes with poor crosslinking around the promoter region were actively transcribed, while transcripts were hardly detected from genes with extensive crosslinking in their promoter regions. For the inducible gene, Il2, the distribution of the promoter shifted in the gradient following T-cell receptor stimulation, consistent with a change in structure at this locus during activation. The kinetics of this switch preceded the chromatin change observed in a DNase I accessibility assay. Thus, this new chromatin fractionation technique has revealed a change in chromatin structure that has not been previously characterized.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chromatin structure and methylation of rat rRNA genes studied by formaldehyde fixation and psoralen cross-linking.Nucleic Acids Res. 1997 May 1;25(9):1727-35. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.9.1727. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997. PMID: 9108154 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin remodeling of the interleukin-2 gene: distinct alterations in the proximal versus distal enhancer regions.Nucleic Acids Res. 1998 Jun 15;26(12):2923-34. doi: 10.1093/nar/26.12.2923. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998. PMID: 9611237 Free PMC article.
-
Formaldehyde crosslinking: a tool for the study of chromatin complexes.J Biol Chem. 2015 Oct 30;290(44):26404-11. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R115.651679. Epub 2015 Sep 9. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26354429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mapping chromosomal proteins in vivo by formaldehyde-crosslinked-chromatin immunoprecipitation.Trends Biochem Sci. 2000 Mar;25(3):99-104. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(99)01535-2. Trends Biochem Sci. 2000. PMID: 10694875 Review.
-
Formaldehyde-assisted isolation of regulatory elements.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2009 Nov-Dec;1(3):400-406. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.36. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2009. PMID: 20046543 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Alterations of epigenetic signatures in hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α deficient mouse liver determined by improved ChIP-qPCR and (h)MeDIP-qPCR assays.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 10;9(1):e84925. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084925. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24427299 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic aspects of floral homeotic genes in relation to sexual dimorphism in the dioecious plant Mercurialis annua.J Exp Bot. 2019 Nov 18;70(21):6245-6259. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erz379. J Exp Bot. 2019. PMID: 31504768 Free PMC article.
-
Two-step binding of transcription factors causes sequential chromatin structural changes at the activated IL-2 promoter.J Immunol. 2011 Sep 15;187(6):3292-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003173. Epub 2011 Aug 10. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21832163 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulation of CYP19 by cohesin-mediated chromosome tethering in human granulosa cells.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2021 Jul 24;27:101086. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2021.101086. eCollection 2021 Sep. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2021. PMID: 34368471 Free PMC article.
-
The Proportion of Chromatin Graded between Closed and Open States Determines the Level of Transcripts Derived from Distinct Promoters in the CYP19 Gene.PLoS One. 2015 May 28;10(5):e0128282. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128282. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26020632 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Noll H, Noll M. Sucrose gradient techniques and applications to nucleosome structure. Methods Enzymol. 1989;170:55–116. - PubMed
-
- Kimura T, Mills FC, Allan J, Gould H. Selective unfolding of erythroid chromatin in the region of the active beta-globin gene. Nature. 1983;306:709–712. - PubMed
-
- Caplan A, Kimura T, Gould H, Allan J. Perturbation of chromatin structure in the region of the adult beta-globin gene in chicken erythrocyte chromatin. J. Mol. Biol. 1987;193:57–70. - PubMed
-
- Sojka DK, Bruniquel D, Schwartz RH, Singh NJ. IL-2 secretion by CD4+ T cells in vivo is rapid, transient, and influenced by TCR-specific competition. J. Immunol. 2004;172:6136–6143. - PubMed
-
- Gilbert N, Boyle S, Fiegler H, Woodfine K, Carter NP, Bickmore WA. Chromatin architecture of the human genome: gene-rich domains are enriched in open chromatin fibers. Cell. 2004;118:555–566. - PubMed

