Identification of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K as a transactivator for human low density lipoprotein receptor gene transcription
- PMID: 20371611
- PMCID: PMC2878543
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.082057
Identification of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K as a transactivator for human low density lipoprotein receptor gene transcription
Abstract
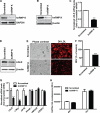
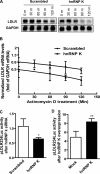
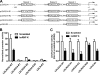
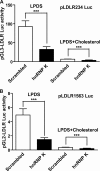
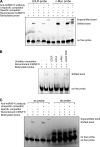
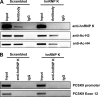
hnRNP K, a member of the family of heterogeneous ribonucleoproteins, is known to exert various functional roles in the nucleus, cytoplasm, and mitochondria to affect different cellular processes including chromatin remodeling, transcription, splicing, and translation. Here we report, for the first time, that hnRNP K is specifically involved in human LDL receptor (LDLR) gene transcription in HepG2 cells. We show that depletion of hnRNP K by siRNA transfection reduces the expression of LDLR mRNA and protein by more than 50% as measured by quantitative real-time PCR and Western blot analysis. Importantly, we show that the decay rate of LDLR mRNA is not affected by hnRNP K siRNA transfection, whereas the LDLR promoter activity is significantly decreased. Furthermore, overexpression of hnRNP K increased the LDLR promoter activity by the luciferase reporter assay. By utilizing a series of mutational and deletional constructs of LDLR promoter luciferase reporters, we mapped the K-responsive element to the repeat 3 (R3) sequence of the LDLR promoter. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays show that the K protein binds to a single-stranded DNA probe containing the CT-rich element of R3, which is in contrast to the requirement of double-stranded DNA for Sp1 to bind to R3. Finally, chromatin immunoprecipitation assays reveal a direct interaction of hnRNP K with the LDLR promoter in intact HepG2 cells. These new findings provide strong evidence demonstrating that hnRNP K is an important transactivator for human LDLR gene transcription. This work sheds new light on our current understanding of how LDLR gene expression is controlled at the transcriptional level.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K represses transcription from a cytosine/thymidine-rich element in the osteocalcin promoter.Biochem J. 2005 Jan 15;385(Pt 2):613-23. doi: 10.1042/BJ20040680. Biochem J. 2005. PMID: 15361071 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulation of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K gene expression.Biochimie. 2015 Feb;109:27-35. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2014.12.002. Epub 2014 Dec 10. Biochimie. 2015. PMID: 25497182 Free PMC article.
-
The critical role of mRNA destabilizing protein heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein d in 3' untranslated region-mediated decay of low-density lipoprotein receptor mRNA in liver tissue.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Jan;34(1):8-16. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.301131. Epub 2013 Oct 24. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 24158514 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K is a transcription factor.Mol Cell Biol. 1996 May;16(5):2350-60. doi: 10.1128/MCB.16.5.2350. Mol Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8628302 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging roles of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K (hnRNP K) in cancer progression.Cancer Lett. 2014 Oct 1;352(2):152-9. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.06.019. Epub 2014 Jul 10. Cancer Lett. 2014. PMID: 25016060 Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatitis C virus stimulates low-density lipoprotein receptor expression to facilitate viral propagation.J Virol. 2014 Mar;88(5):2519-29. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02727-13. Epub 2013 Dec 18. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24352472 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation mediated regulation of RNA splicing in plants.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Sep 14;14:1249057. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1249057. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37780493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo rescue of alveolar macrophages from SP-A knockout mice with exogenous SP-A nearly restores a wild type intracellular proteome; actin involvement.Proteome Sci. 2011 Oct 28;9:67. doi: 10.1186/1477-5956-9-67. Proteome Sci. 2011. PMID: 22035134 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in the response of the alveolar macrophage proteome to treatment with exogenous surfactant protein-A.Proteome Sci. 2012 Jul 23;10(1):44. doi: 10.1186/1477-5956-10-44. Proteome Sci. 2012. PMID: 22824420 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix metalloproteinase 12 is induced by heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K and promotes migration and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2014 May 20;14:348. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-348. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24885469 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

