CNS expression of anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-4 attenuates Alzheimer's disease-like pathogenesis in APP+PS1 bigenic mice
- PMID: 20371618
- PMCID: PMC2909296
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.10-155317
CNS expression of anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-4 attenuates Alzheimer's disease-like pathogenesis in APP+PS1 bigenic mice
Abstract
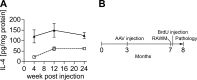
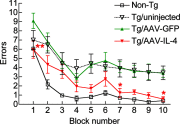
Cytokines play an emerging role as neurotransmitters, neuromodulators, and neurohormones in the brain. This paradigm shift in cytokine function offers a new framework to understand their roles in ameliorating neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer's disease (AD). Molecular adjuvant therapy of AD animal models with glatiramer acetate induces anti-inflammatory responses and therapeutic effects. Although these effects are potentially mediated through anti-inflammatory cytokine signaling, the exact molecular identities and pathways are poorly understood. Here, we show that virus-mediated expression of the mouse interleukin (IL)-4 gene in beta-amyloid precursor protein + presenilin-1 (APP+PS1) bigenic mice attenuates AD pathogenesis. Introduction of an adeno-associated viral (AAV) vector encoding IL-4 into the hippocampus resulted in sustained expression of IL-4, reduced astro/microgliosis, amyloid-beta peptide (Abeta) oligomerization and deposition, and enhanced neurogenesis. Moreover, increased levels of IL-4 improved spatial learning, promoted phosphorylation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit 2B at Tyr 1472, and enhanced its cell surface retention both in vivo and in vitro. Our data suggest that neuronal anti-inflammatory cytokine signaling may be a potential alternative target for non-Abeta-mediated treatment of AD.
Figures

Similar articles
-
AAV serotype 2/1-mediated gene delivery of anti-inflammatory interleukin-10 enhances neurogenesis and cognitive function in APP+PS1 mice.Gene Ther. 2012 Jul;19(7):724-33. doi: 10.1038/gt.2011.126. Epub 2011 Sep 15. Gene Ther. 2012. PMID: 21918553 Free PMC article.
-
Urolithin A attenuates memory impairment and neuroinflammation in APP/PS1 mice.J Neuroinflammation. 2019 Mar 14;16(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1450-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2019. PMID: 30871577 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term treadmill exercise inhibits the progression of Alzheimer's disease-like neuropathology in the hippocampus of APP/PS1 transgenic mice.Behav Brain Res. 2013 Nov 1;256:261-72. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2013.08.008. Epub 2013 Aug 19. Behav Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23968591
-
Intramuscular delivery of p75NTR ectodomain by an AAV vector attenuates cognitive deficits and Alzheimer's disease-like pathologies in APP/PS1 transgenic mice.J Neurochem. 2016 Jul;138(1):163-73. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13616. Epub 2016 Jun 6. J Neurochem. 2016. PMID: 26991827
-
Dihydromyricetin inhibits microglial activation and neuroinflammation by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation in APP/PS1 transgenic mice.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2018 Dec;24(12):1207-1218. doi: 10.1111/cns.12983. Epub 2018 Jun 4. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2018. PMID: 29869390 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The classification of microglial activation phenotypes on neurodegeneration and regeneration in Alzheimer's disease brain.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2012 Aug;60(4):251-66. doi: 10.1007/s00005-012-0181-2. Epub 2012 Jun 19. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2012. PMID: 22710659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of microglial activation protects hippocampal neurogenesis and improves cognitive deficits in a transgenic mouse model for Alzheimer's disease.Neurodegener Dis. 2012;9(4):187-98. doi: 10.1159/000330363. Epub 2012 May 8. Neurodegener Dis. 2012. PMID: 22584394 Free PMC article.
-
Microglial phenotype and adaptation.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013 Sep;8(4):807-23. doi: 10.1007/s11481-013-9490-4. Epub 2013 Jul 25. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23881706 Review.
-
Gene therapy for misfolding protein diseases of the central nervous system.Neurotherapeutics. 2013 Jul;10(3):498-510. doi: 10.1007/s13311-013-0191-8. Neurotherapeutics. 2013. PMID: 23700209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mapping the Plasticity of Morphology, Molecular Properties and Function in Mouse Primary Microglia.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Jan 26;15:811061. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.811061. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35153675 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Selkoe D. J. The molecular pathology of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron. 1991;6:487–498. - PubMed
-
- Schenk D., Barbour R., Dunn W., Gordon G., Grajeda H., Guido T., Hu K., Huang J., Johnson-Wood K., Khan K., Kholodenko D., Lee M., Liao Z., Lieberburg I., Motter R., Mutter L., Soriano F., Shopp G., Vasquez N., Vandevert C., Walker S., Wogulis M., Yednock T., Games D., Seubert P. Immunization with amyloid-beta attenuates Alzheimer-disease-like pathology in the PDAPP mouse. Nature. 1999;400:173–177. - PubMed
-
- Morgan D., Diamond D. M., Gottschall P. E., Ugen K. E., Dickey C., Hardy J., Duff K., Jantzen P., DiCarlo G., Wilcock D., Connor K., Hatcher J., Hope C., Gordon M., Arendash G. W. A beta peptide vaccination prevents memory loss in an animal model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nature. 2000;408:982–985. - PubMed
-
- Bard F., Barbour R., Cannon C., Carretto R., Fox M., Games D., Guido T., Hoenow K., Hu K., Johnson-Wood K., Khan K., Kholodenko D., Lee C., Lee M., Motter R., Nguyen M., Reed A., Schenk D., Tang P., Vasquez N., Seubert P., Yednock T. Epitope and isotype specificities of antibodies to beta-amyloid peptide for protection against Alzheimer’s disease-like neuropathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:2023–2028. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hock C., Konietzko U., Streffer J. R., Tracy J., Signorell A., Muller-Tillmanns B., Lemke U., Henke K., Moritz E., Garcia E., Wollmer M. A., Umbricht D., de Quervain D. J., Hofmann M., Maddalena A., Papassotiropoulos A., Nitsch R. M. Antibodies against beta-amyloid slow cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron. 2003;38:547–554. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

