Survival of patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma treated with radiation and temozolomide in research studies in the United States
- PMID: 20371685
- PMCID: PMC2861898
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-3106
Survival of patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma treated with radiation and temozolomide in research studies in the United States
Abstract
Purpose: Novel agents are currently combined with radiation and temozolomide (RT + TMZ) in newly diagnosed glioblastoma using overall survival as the primary end point. Results of these phase II studies are typically compared with the phase III European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) survival data that resulted in RT + TMZ becoming standard therapy.
Experimental design: The New Approaches to Brain Tumor Therapy (NABTT) Consortium assigned 365 patients with glioblastoma to four single-cohort studies with similar eligibility criteria. Patients received RT + TMZ with talampanel (n = 72), poly-ICLC (n = 97), or cilengitide (n = 112) or RT + TMZ alone with monitoring of CD4 counts (n = 84). Overall survival of those ages 18 to 70 years with glioblastoma was compared with published EORTC data.
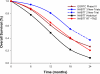
Results: NABTT and EORTC patients had comparable performance status and debulking surgery. Median, 12-month, and 24-month survival rates for the EORTC patients (n = 287) and the comparable NABTT patients receiving RT + TMZ and novel agents (n = 244) are 14.6 versus 19.6 months, 61% versus 81%, and 27% versus 37%, respectively. This represents a 37% reduction in odds of death (P < 0.0001) through 2 years of follow-up. NABTT and EORTC patients receiving only RT + TMZ had similar survival.
Conclusions: Newly diagnosed glioblastoma treated recently with RT + TMZ and talampanel, poly-ICLC, or cilengitide had significantly longer survival than similar patients treated with only RT + TMZ accrued internationally from 2000 to 2002. These differences could result from the novel agents or changing patterns of care. Until the reasons for these different survival rates are clarified, comparisons of outcomes from phase II studies with published RT + TMZ survival data should be interpreted with caution.
Figures
References
-
- Laperriere N, Zuraw L, Cairncross G, Cancer Care Ontario Practice Guidelines Initiative Neuro-Oncology Disease Site Group Radiotherapy for newly diagnosed malignant glioma in adults: A systematic review. Radiother Oncol. 2002;64:259–73. - PubMed
-
- Stewart LA. Chemotherapy in adult high-grade glioma: A systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data from 12 randomised trials. Lancet. 2002;359:1011–8. - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:987–96. - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:459–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

