Glycogen synthase kinase-3 plays a central role in mediating glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis
- PMID: 20371704
- PMCID: PMC5417474
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2009-0466
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 plays a central role in mediating glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis
Abstract
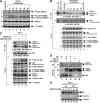
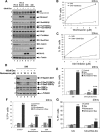
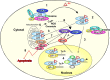
It is still unclear how glucocorticoids (GCs) induce apoptosis of thymocytes and T lymphoma cells. Emergence of GC-resistant lymphoma cells is a major obstacle in GC therapy, emphasizing the need for novel strategies that maintain the sensitivity of lymphoma cells to the proapoptotic effects of GC. We have undertaken a kinome study to elucidate the signal transduction pathways involved in mediating GC-induced apoptosis. Our study shows that glycogen synthase kinase (GSK3) plays a central role in promoting GC-induced apoptosis. In the absence of a ligand, GSK3alpha, but not GSK3beta, is sequestered to the glucocorticoid receptor (GR). Exposure to GCs leads to dissociation of GSK3alpha from GR and subsequent interaction of GSK3alpha and GSK3beta with the proapoptotic Bim protein, an essential mediator of GC-induced apoptosis. Chemical inhibition of GSK3 by SB216763, BIO-Acetoxime, or LiCl and GSK3 inhibition using a dominant-negative mutant of GSK3 impede this cell death process, indicating that GSK3 is involved in transmitting the apoptotic signal. GC resistance in lymphoma cells can be relieved by inhibiting the phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase-Akt survival pathway, which inactivates GSK3. Notch1, a transcription factor frequently activated in T acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells, confers GC resistance through activation of Akt. Altogether, this study illuminates the link connecting upstream GR signals to the downstream mediators of GC-induced apoptosis. Our data suggest that targeting protein kinases involved in GSK3 inactivation should improve the outcome of GC therapy.
Figures





Similar articles
-
[The kinome and glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis].Ai Zheng. 2008 Nov;27(11):1121-9. Ai Zheng. 2008. PMID: 19000440 Chinese.
-
Glucocorticoid-mediated BIM induction and apoptosis are regulated by Runx2 and c-Jun in leukemia cells.Cell Death Dis. 2012 Jul 19;3(7):e349. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2012.89. Cell Death Dis. 2012. PMID: 22825467 Free PMC article.
-
Glycogen synthase kinase-3β is involved in ligand-dependent activation of transcription and cellular localization of the glucocorticoid receptor.Mol Endocrinol. 2012 Sep;26(9):1508-20. doi: 10.1210/me.2011-1366. Epub 2012 Jul 6. Mol Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22771494 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase networks regulating glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis of hematopoietic cancer cells: fundamental aspects and practical considerations.Leuk Lymphoma. 2010 Nov;51(11):1968-2005. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2010.506570. Epub 2010 Sep 20. Leuk Lymphoma. 2010. PMID: 20849387 Review.
-
New insights into Notch1 regulation of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR1 signaling axis: targeted therapy of γ-secretase inhibitor resistant T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Cell Signal. 2014 Jan;26(1):149-61. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.09.021. Epub 2013 Oct 16. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24140475 Review.
Cited by
-
Budesonide and fluticasone propionate differentially affect the airway epithelial barrier.Respir Res. 2016 Jan 6;17:2. doi: 10.1186/s12931-015-0318-z. Respir Res. 2016. PMID: 26739349 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs and Glucocorticoid-Induced Apoptosis in Lymphoid Malignancies.ISRN Hematol. 2013;2013:348212. doi: 10.1155/2013/348212. Epub 2013 Jan 29. ISRN Hematol. 2013. PMID: 23431463 Free PMC article.
-
Progesterone receptor A stability is mediated by glycogen synthase kinase-3β in the Brca1-deficient mammary gland.J Biol Chem. 2013 Sep 6;288(36):26265-26274. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.476556. Epub 2013 Jul 23. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23880761 Free PMC article.
-
Dual inhibition of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL strikingly enhances PI3K inhibition-induced apoptosis in human myeloid leukemia cells through a GSK3- and Bim-dependent mechanism.Cancer Res. 2013 Feb 15;73(4):1340-51. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-1365. Epub 2012 Dec 12. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23243017 Free PMC article.
-
Glycogen synthase kinase-3β modulation of glucocorticoid responsiveness in COPD.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015 Nov 15;309(10):L1112-23. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00077.2015. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26320152 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sionov RV, Kfir S, Zafrir E, Cohen O, Zilberman Y, Yefenof E2006. Glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis revisited: a novel role for glucocorticoid receptor translocation to the mitochondria. Cell Cycle 5:1017–1026 - PubMed
-
- Sionov RV, Spokoini R, Kfir-Erenfeld S, Cohen O, Yefenof E2008. Mechanisms regulating the susceptibility of hematopoietic malignancies to glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis. Adv Cancer Res 101:127–248 - PubMed
-
- Wang Z, Malone MH, He H, McColl KS, Distelhorst CW2003. Microarray analysis uncovers the induction of the proapoptotic BH3-only protein Bim in multiple models of glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 278:23861–23867 - PubMed
-
- Puthalakath H, Strasser A2002. Keeping killers on a tight leash: transcriptional and post-translational control of the pro-apoptotic activity of BH3-only proteins. Cell Death Differ 9:505–512 - PubMed
-
- Haller J, Mikics E, Makara GB2008. The effects of non-genomic glucocorticoid mechanisms on bodily functions and the central neural system. A critical evaluation of findings. Front Neuroendocrinol 29:273–291 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

