Bridging the gap between cytotoxic and biologic therapy with metronomic topotecan and pazopanib in ovarian cancer
- PMID: 20371710
- PMCID: PMC2852465
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-0967
Bridging the gap between cytotoxic and biologic therapy with metronomic topotecan and pazopanib in ovarian cancer
Abstract
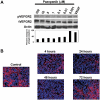
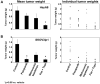
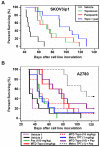
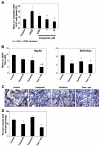
This study aimed to investigate the antitumor and antiangiogenic effects utilizing a novel therapy regimen of metronomic topotecan and pazopanib, a multireceptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor. In vitro (Western blot) and in vivo dose-finding experiments were done following pazopanib therapy in ovarian cancer models. Pazopanib and metronomic (daily) oral topotecan therapy was examined in an orthotopic model of ovarian cancer. Tumor weights, survival, and markers of the tumor microenvironment [angiogenesis (CD31 and pericyte coverage), proliferation (Ki-67), and apoptosis (terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling)] were analyzed by immunostaining following therapy. Pazopanib therapy reduced vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR-2) activity in vitro and vivo in a dose-dependent manner. Compared with control mice, pazopanib reduced tumor weight by 28% to 82% (P < 0.01 in the SKOV3ip1 model) and metronomic topotecan reduced tumor weight by 40% to 59% in the HeyA8 (P = 0.13) and SKOV3ip1 (P = 0.07) models. Combination therapy had the greatest effect with 79% to 84% reduction (P < 0.01 for both models). In the SKOV3ip1 and A2780 models, mouse survival was significantly longer (P < 0.001 versus controls) with pazopanib and metronomic topotecan therapy. Pazopanib therapy reduced murine endothelial cell migration in vitro in a dose-dependent manner following VEGF stimulation and decreased tumor microvessel density and pericyte coverage when given in combination with metronomic topotecan. Tumor cell proliferation decreased in all treatment arms compared with controls (P < 0.01 for combination groups) and increased tumor cell apoptosis by 4-fold with combination therapy. Pazopanib therapy in combination with metronomic topotecan therapy showed significant antitumor and antiangiogenic properties in preclinical ovarian cancer models and warrants further investigation as a novel therapeutic regimen in clinical trials. Mol Cancer Ther; 9(4); 985-95. (c)2010 AACR.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Potent preclinical impact of metronomic low-dose oral topotecan combined with the antiangiogenic drug pazopanib for the treatment of ovarian cancer.Mol Cancer Ther. 2010 Apr;9(4):996-1006. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-0960. Epub 2010 Apr 6. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010. PMID: 20371722 Free PMC article.
-
Metronomic oral topotecan with pazopanib is an active antiangiogenic regimen in mouse models of aggressive pediatric solid tumor.Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Sep 1;17(17):5656-67. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0078. Epub 2011 Jul 25. Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21788355 Free PMC article.
-
Dual Metronomic Chemotherapy with Nab-Paclitaxel and Topotecan Has Potent Antiangiogenic Activity in Ovarian Cancer.Mol Cancer Ther. 2015 Dec;14(12):2677-86. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0630. Epub 2015 Oct 29. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015. PMID: 26516159 Free PMC article.
-
Pazopanib in ovarian cancer.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2015;15(9):995-1005. doi: 10.1586/14737140.2015.1081383. Epub 2015 Aug 20. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2015. PMID: 26296187 Review.
-
(Pre-)clinical pharmacology and activity of pazopanib, a novel multikinase angiogenesis inhibitor.Oncologist. 2010;15(6):539-47. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2009-0274. Epub 2010 May 28. Oncologist. 2010. PMID: 20511320 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metronomics as maintenance treatment in oncology: time for chemo-switch.Front Oncol. 2014 Apr 10;4:76. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00076. eCollection 2014. Front Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24782987 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
An in vitro assessment of liposomal topotecan simulating metronomic chemotherapy in combination with radiation in tumor-endothelial spheroids.Sci Rep. 2015 Oct 15;5:15236. doi: 10.1038/srep15236. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26468877 Free PMC article.
-
In Vivo Assessment of Ovarian Tumor Response to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Pazopanib by Using Hyperpolarized 13C-Pyruvate MR Spectroscopy and 18F-FDG PET/CT Imaging in a Mouse Model.Radiology. 2017 Dec;285(3):830-838. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2017161772. Epub 2017 Jul 13. Radiology. 2017. PMID: 28707963 Free PMC article.
-
The role of endothelial cell-pericyte interactions in vascularization and diseases.J Adv Res. 2025 Jan;67:269-288. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.01.016. Epub 2024 Jan 20. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 38246244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metronomic oral topotecan prolongs survival and reduces liver metastasis in improved preclinical orthotopic and adjuvant therapy colon cancer models.Gut. 2013 Feb;62(2):259-71. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2011-301585. Epub 2012 Apr 28. Gut. 2013. PMID: 22543158 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med. 1971;285:1182–6. - PubMed
-
- Spannuth WA, Sood AK, Coleman RL. Angiogenesis as a strategic target for ovarian cancer therapy. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 2008;5:194–204. - PubMed
-
- McGuire WP, Hoskins WJ, Brady MF, Kucera PR, Partridge EE, Look KY, et al. Cyclophosphamide and cisplatin compared with paclitaxel and cisplatin in patients with stage III and stage IV ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:1–6. - PubMed
-
- Kerbel RS, Kamen BA. The anti-angiogenic basis of metronomic chemotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:423–36. - PubMed
-
- Garcia AA, Hirte H, Fleming G, Yang D, Tsao-Wei DD, Roman L, et al. Phase II clinical trial of bevacizumab and low-dose metronomic oral cyclophosphamide in recurrent ovarian cancer: a trial of the California, Chicago, and Princess Margaret Hospital phase II consortia. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:76–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

