Potent preclinical impact of metronomic low-dose oral topotecan combined with the antiangiogenic drug pazopanib for the treatment of ovarian cancer
- PMID: 20371722
- PMCID: PMC2852477
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-0960
Potent preclinical impact of metronomic low-dose oral topotecan combined with the antiangiogenic drug pazopanib for the treatment of ovarian cancer
Abstract
Low-dose metronomic chemotherapy has shown promising activity in many preclinical and some phase II clinical studies involving various tumor types. To evaluate further the potential therapeutic impact of metronomic chemotherapy for ovarian cancer, we developed a preclinical model of advanced human ovarian cancer and tested various low-dose metronomic chemotherapy regimens alone or in concurrent combination with an antiangiogenic drug, pazopanib. Clones of the SKOV-3 human ovarian carcinoma cell line expressing a secretable beta-subunit of human choriogonadotropic (beta-hCG) protein and firefly luciferase were generated and evaluated for growth after orthotopic (i.p.) injection into severe combined immunodeficient mice; a highly aggressive clone, SKOV-3-13, was selected for further study. Mice were treated beginning 10 to 14 days after injection of cells when evidence of carcinomatosis-like disease in the peritoneum was established as assessed by imaging analysis. Chemotherapy drugs tested for initial experiments included oral cyclophosphamide, injected irinotecan or paclitaxel alone or in doublet combinations with cyclophosphamide; the results indicated that metronomic cyclophosphamide had no antitumor activity whereas metronomic irinotecan had potent activity. We therefore tested an oral topoisomerase-1 inhibitor, oral topotecan, at optimal biological dose of 1 mg/kg/d. Metronomic oral topotecan showed excellent antitumor activity, the extent of which was significantly enhanced by concurrent pazopanib, which itself had only modest activity, with 100% survival values of the drug combination after six months of continuous therapy. In conclusion, oral topotecan may be an ideal agent to consider for clinical trial assessment of metronomic chemotherapy for ovarian cancer, especially when combined with an antiangiogenic drug targeting the vascular endothelial growth factor pathway, such as pazopanib. Mol Cancer Ther; 9(4); 996-1006. (c)2010 AACR.
Figures
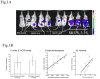
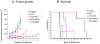
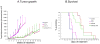
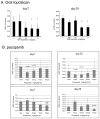


References
-
- Browder T, Butterfield CE, Kraling BM, Marshall B, O’Reilly MS, Folkman J. Antiangiogenic scheduling of chemotherapy improves efficacy against experimental drug-resistant cancer. Cancer Res. 2000;60:1878–86. - PubMed
-
- Kerbel RS, Kamen BA. Antiangiogenic basis of low-dose metronomic chemotherapy. Nature Rev Cancer. 2004;4:423–36. - PubMed
-
- Ghiringhelli F, Larmonier N, Schmitt E, Parcellier A, Cathelin D, Garrido C, et al. CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells suppress tumor immunity but are sensitive to cyclophosphamide which allows immunotherapy of established tumors to be curative. Eur J Immunol. 2004;34:336–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

