In vivo deletion of immunoglobulin domains 5 and 6 in neurofascin (Nfasc) reveals domain-specific requirements in myelinated axons
- PMID: 20371806
- PMCID: PMC2856701
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5951-09.2010
In vivo deletion of immunoglobulin domains 5 and 6 in neurofascin (Nfasc) reveals domain-specific requirements in myelinated axons
Abstract
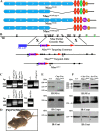
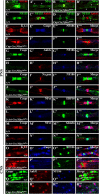
The formation of paranodal axo-glial junctions is critical for the rapid and efficient propagation of nerve impulses. Genetic ablation of genes encoding the critical paranodal proteins Caspr, contactin (Cont), and the myelinating glia-specific isoform of Neurofascin (Nfasc(NF155)) results in the disruption of the paranodal axo-glial junctions, loss of ion channel segregation, and impaired nerve conduction, but the mechanisms regulating their interactions remain elusive. Here, we report that loss of immunoglobulin (Ig) domains 5 and 6 in Nfasc(NF155) in mice phenocopies complete ablation of Nfasc(NF155). The mutant mice lack paranodal septate junctions, resulting in the diffusion of Caspr and Cont from the paranodes, and redistribution of the juxtaparanodal potassium channels toward the nodes. Although critical for Nfasc(NF155) function, we find that Ig5-6 are dispensable for nodal Nfasc(NF186) function. Moreover, in vitro binding assays using Ig5-6 deletion constructs reveal their importance for the association of Nfasc(NF155) with Cont. These findings provide the first molecular evidence demonstrating domain-specific requirements controlling the association of the paranodal tripartite complex in vivo. Our studies further emphasize that in vivo structure/function analysis is necessary to define the unique protein-protein interactions that differentially regulate the functions of Neurofascins during axonal domain organization.
Figures


References
-
- Bhat MA, Rios JC, Lu Y, Garcia-Fresco GP, Ching W, St Martin M, Li J, Einheber S, Chesler M, Rosenbluth J, Salzer JL, Bellen HJ. Axon-glia interactions and the domain organization of myelinated axons requires neurexin IV/Caspr/Paranodin. Neuron. 2001;30:369–383. - PubMed
-
- Boyle ME, Berglund EO, Murai KK, Weber L, Peles E, Ranscht B. Contactin orchestrates assembly of the septate-like junctions at the paranode in myelinated peripheral nerve. Neuron. 2001;30:385–397. - PubMed
-
- Charles P, Tait S, Faivre-Sarrailh C, Barbin G, Gunn-Moore F, Denisenko-Nehrbass N, Guennoc AM, Girault JA, Brophy PJ, Lubetzki C. Neurofascin is a glial receptor for the paranodin/Caspr-contactin axonal complex at the axoglial junction. Curr Biol. 2002;12:217–220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
