Structural plasticity underlies experience-dependent functional plasticity of cortical circuits
- PMID: 20371813
- PMCID: PMC2910869
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6403-09.2010
Structural plasticity underlies experience-dependent functional plasticity of cortical circuits
Abstract
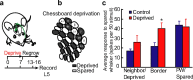
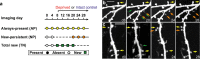
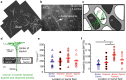
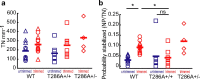
The stabilization of new spines in the barrel cortex is enhanced after whisker trimming, but its relationship to experience-dependent plasticity is unclear. Here we show that in wild-type mice, whisker potentiation and spine stabilization are most pronounced for layer 5 neurons at the border between spared and deprived barrel columns. In homozygote alphaCaMKII-T286A mice, which lack experience-dependent potentiation of responses to spared whiskers, there is no increase in new spine stabilization at the border between barrel columns after whisker trimming. Our data provide a causal link between new spine synapses and plasticity of adult cortical circuits and suggest that alphaCaMKII autophosphorylation plays a role in the stabilization but not formation of new spines.
Figures
References
-
- Feng G, Mellor RH, Bernstein M, Keller-Peck C, Nguyen QT, Wallace M, Nerbonne JM, Lichtman JW, Sanes JR. Imaging neuronal subsets in transgenic mice expressing multiple spectral variants of GFP. Neuron. 2000;28:41–51. - PubMed
-
- Fox K, Wong RO. A comparison of experience-dependent plasticity in the visual and somatosensory systems. Neuron. 2005;48:465–477. - PubMed
-
- Giese KP, Fedorov NB, Filipkowski RK, Silva AJ. Autophosphorylation at Thr286 of the alpha calcium-calmodulin kinase II in LTP and learning. Science. 1998;279:870–873. - PubMed
-
- Glazewski S, Fox K. Time course of experience-dependent synaptic potentiation and depression in barrel cortex of adolescent rats. J Neurophysiol. 1996;75:1714–1729. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
