Pup grows up: in vitro characterization of the degradation of pupylated proteins
- PMID: 20372178
- PMCID: PMC2857470
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2010.40
Pup grows up: in vitro characterization of the degradation of pupylated proteins
Abstract
By reconstituting the recently discovered prokaryotic ubiquitin-like protein (Pup)--proteasome degradation system in vitro, Weber-Ban and colleagues (Striebel et al, 2010) elucidate its mechanism and describe a surprising variation on the established principles of protease targeting. Nevertheless, their findings suggest that the bacterial and eukaryotic systems follow the same overall principles even if the details differ.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
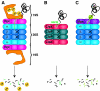
Comment on
-
The mycobacterial Mpa-proteasome unfolds and degrades pupylated substrates by engaging Pup's N-terminus.EMBO J. 2010 Apr 7;29(7):1262-71. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2010.23. Epub 2010 Mar 4. EMBO J. 2010. PMID: 20203624 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

