Inhibition of NF-kappaB and Akt pathways by an antibody-avidin fusion protein sensitizes malignant B-cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis
- PMID: 20372806
- PMCID: PMC3732793
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo_00000615
Inhibition of NF-kappaB and Akt pathways by an antibody-avidin fusion protein sensitizes malignant B-cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis
Abstract
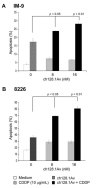
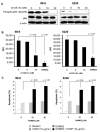
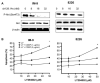
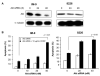
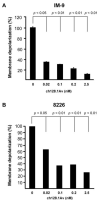
Multiple myeloma (MM) is an incurable disease of malignant plasma cells. Recent therapeutic advancements have resulted in improved response rates, however, there is no improvement in overall survival, therefore, new therapeutics are needed. Since the transferrin receptor is upregulated on the surface of MM cells, we previously developed an antibody fusion protein consisting of an IgG3 specific for the human transferrin receptor 1 (TfR1, CD71) genetically fused to avidin at its carboxy-terminus (ch128.1Av). We have previously shown that ch128.1Av exhibits intrinsic cytotoxicity against certain malignant B-cells by disrupting the cycling of the TfR and decreasing TfR cell surface expression resulting in lethal iron starvation. In addition, ch128.1Av can sensitize malignant cells to apoptosis induced by gambogic acid, a herbal drug used in Chinese medicine. In this study, we hypothesized that ch128.1Av may also sensitize drug-resistant malignant B-cells to chemotherapeutic agents by inhibiting key survival pathways. In this study we show that ch128.1Av sensitizes malignant B-cells to apoptosis induced by cisplatin (CDDP). The sensitization by ch128.1Av resulted in the inhibition of the constitutively activated Akt and NF-kappaB survival/antiapoptotic pathways and downstream decreased expression of antiapoptotic gene products such as BclxL and survivin. The direct role of the inhibition of the Akt and NF-kappaB pathways by ch128.1Av in CDDP-mediated cytotoxicity was demonstrated by the use of specific chemical inhibitors and siRNA which mimicked the effects of ch128.1Av. Overall, this study provides evidence of the therapeutic potential of ch128.1Av as a chemo-sensitizing agent in drug-resistant tumor cells.
Figures

References
-
- Sloan B, Scheinfeld NS. Pazopanib, a VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor for cancer therapy. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2008;9:1324–1335. - PubMed
-
- Law CL, Gordon KA, Collier J, et al. Preclinical antilymphoma activity of a humanized anti-CD40 monoclonal antibody, SGN-40. Cancer Res. 2005;65:8331–8338. - PubMed
-
- Lee JH, Koo TH, Yoon H, et al. Inhibition of NF-kappa B activation through targeting I kappa B kinase by celastrol, a quinone methide triterpenoid. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006;72:1311–1321. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe M, Dewan MZ, Okamura T, et al. A novel NF-kappaB inhibitor DHMEQ selectively targets constitutive NF-kappaB activity and induces apoptosis of multiple myeloma cells in vitro and in vivo. Int J Cancer. 2005;114:32–38. - PubMed
-
- Tatetsu H, Okuno Y, Nakamura M, et al. Dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin, a novel nuclear factor-kappaB inhibitor, induces apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells in an IkappaBalpha-independent manner. Mol Cancer Ther. 2005;4:1114–1120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

