Dengue virus life cycle: viral and host factors modulating infectivity
- PMID: 20372965
- PMCID: PMC11115823
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-010-0357-z
Dengue virus life cycle: viral and host factors modulating infectivity
Abstract
Dengue virus (DENV 1-4) represents a major emerging arthropod-borne pathogen. All four DENV serotypes are prevalent in the (sub) tropical regions of the world and infect 50-100 million individuals annually. Whereas the majority of DENV infections proceed asymptomatically or result in self-limited dengue fever, an increasing number of patients present more severe manifestations, such as dengue hemorrhagic fever and dengue shock syndrome. In this review we will give an overview of the infectious life cycle of DENV and will discuss the viral and host factors that are important in controlling DENV infection.
Figures



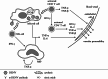
References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO report on global surveillance of epidemic-prone infectious diseases—dengue and dengue haemorrhagic fever. World Health Organization. http://www.who.int/csr/resources/publications/dengue/CSR_ISR_2000_1/en/. Accessed 9 March 2010
-
- Burke DS, Monath TP. Flaviviruses. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Fields virology. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2001. pp. 1043–1125.
-
- Burke DS, Nisalak A, Johnson DE, Scott RM. A prospective study of dengue infections in Bangkok. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988;38:172–180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

