Preclinical characterization of atiprimod, a novel JAK2 AND JAK3 inhibitor
- PMID: 20372971
- PMCID: PMC4170651
- DOI: 10.1007/s10637-010-9429-z
Preclinical characterization of atiprimod, a novel JAK2 AND JAK3 inhibitor
Abstract
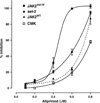
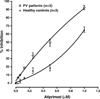
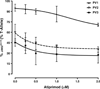
We herein report on the activity of the JAK2/JAK3 small molecule inhibitor atiprimod on mouse FDCP-EpoR cells carrying either wild-type (JAK2 (WT)) or mutant (JAK2 (V617F)) JAK2, human acute megakaryoblastic leukemia cells carrying JAK2 (V617F) (SET-2 cell line), and human acute megakaryocytic leukemia carrying mutated JAK3 (CMK cells). Atiprimod inhibited more efficaciously the proliferation of FDCP-EpoR JAK2 (V617F) (IC(50) 0.42 μM) and SET-2 cells (IC(50) 0.53 μM) than that of CMK (IC(50) 0.79 μM) or FDCP-EpoR JAK2 (WT) cells (IC(50) 0.69 μM). This activity was accompanied by inhibition of the phosphorylation of JAK2 and downstream signaling proteins STAT3, STAT5, and AKT in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Atiprimod-induced cell growth inhibition of JAK2 (V617F)-positive cells was coupled with induction of apoptosis, as evidenced by heightened mitochondrial membrane potential and caspase-3 activity, as well as PARP cleavage, increased turnover of the anti-apoptotic X-linked mammalian inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) protein, and inhibition of the pro-apoptotic protein BCL-2 in a time- and dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, atiprimod was more effective at inhibiting the proliferation of peripheral blood hematopoietic progenitors obtained from patients with JAK2 (V617F)-positive polycythemia vera than at inhibiting hematopoietic progenitors from normal individuals (p = 0.001). The effect on primary expanded erythroid progenitors was paralleled by a decrease in JAK2(V617F) mutant allele burden in single microaspirated BFU-E and CFU-GM colonies. Taken together, our data supports the clinical testing of atiprimod in patients with hematologic malignancies driven by constitutive activation of JAK2 or JAK3 kinases.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The JAK kinase inhibitor CP-690,550 suppresses the growth of human polycythemia vera cells carrying the JAK2V617F mutation.Cancer Sci. 2008 Jun;99(6):1265-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.00817.x. Cancer Sci. 2008. PMID: 18482053 Free PMC article.
-
Bone marrow stroma-secreted cytokines protect JAK2(V617F)-mutated cells from the effects of a JAK2 inhibitor.Cancer Res. 2011 Jun 1;71(11):3831-40. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-4002. Epub 2011 Apr 21. Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21512135 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and evaluation of ZT55, a novel highly-selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor of JAK2V617F against myeloproliferative neoplasms.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Feb 4;38(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1062-x. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30717771 Free PMC article.
-
JAK2, the JAK2 V617F mutant and cytokine receptors.Pathol Biol (Paris). 2007 Mar;55(2):88-91. doi: 10.1016/j.patbio.2006.06.003. Epub 2006 Aug 14. Pathol Biol (Paris). 2007. PMID: 16904848 Review.
-
Inhibitors of JAK2 and JAK3: an update on the patent literature 2010 - 2012.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2013 Apr;23(4):449-501. doi: 10.1517/13543776.2013.765862. Epub 2013 Feb 1. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2013. PMID: 23367873 Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor-related interleukins: old validated targets for new anti-cancer drug development.Mol Cancer. 2017 Sep 19;16(1):153. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0721-9. Mol Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28927416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peripancreatic paraganglioma: Lesson from a round table.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Jun 7;28(21):2396-2402. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i21.2396. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35800185 Free PMC article.
-
Second-Generation Jak2 Inhibitors for Advanced Prostate Cancer: Are We Ready for Clinical Development?Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 17;13(20):5204. doi: 10.3390/cancers13205204. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34680353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A newly identified 45-kDa JAK2 variant with an altered kinase domain structure represents a novel mode of JAK2 kinase inhibitor resistance.Mol Oncol. 2024 Feb;18(2):415-430. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13566. Epub 2023 Dec 20. Mol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38104968 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a novel azaspirane that targets the Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo.J Biol Chem. 2014 Dec 5;289(49):34296-307. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.601104. Epub 2014 Oct 15. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25320076 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Spivak JL. The chronic myeloproliferative disorders: clonality and clinical heterogeneity. Semin Hematol. 2004;41:1–5. - PubMed
-
- James C, Ugo V, Le Couedic JP, et al. A unique clonal JAK2 mutation leading to constitutive signalling causes polycythaemia vera. Nature. 2005;434:1144–1148. - PubMed
-
- Lucet IS, Fantino E, Styles M, et al. The structural basis of Janus kinase 2 inhibition by a potent and specific pan-Janus kinase inhibitor. Blood. 2006;107:176–183. - PubMed
-
- Silva M, Richard C, Benito A, Sanz C, Olalla I, Fernandez-Luna JL. Expression of Bcl-x in erythroid precursors from patients with polycythemia vera. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:564–571. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

