Orphan nuclear receptors as targets for drug development
- PMID: 20372994
- PMCID: PMC3518931
- DOI: 10.1007/s11095-010-0117-7
Orphan nuclear receptors as targets for drug development
Abstract
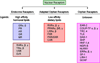
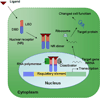
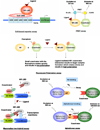
Orphan nuclear receptors regulate diverse biological processes. These important molecules are ligand-activated transcription factors that act as natural sensors for a wide range of steroid hormones and xenobiotic ligands. Because of their importance in regulating various novel signaling pathways, recent research has focused on identifying xenobiotics targeting these receptors for the treatment of multiple human diseases. In this review, we will highlight these receptors in several physiologic and pathophysiologic actions and demonstrate how their functions can be exploited for the successful development of newer drugs.
Figures

References
-
- Giguere V. Orphan nuclear receptors: from gene to function. Endocr Rev. 1999;20:689–725. - PubMed
-
- Laudet V. Evolution of the nuclear receptor superfamily: early diversification from an ancestral orphan receptor. J Mol Endocrino. 1997;19:207–226. - PubMed
-
- Jensen EV. Estrogen receptor: ambiguities in the use of this term. Science. 1968;159:1261. - PubMed
-
- Horwitz KB, Jackson TA, Bain DL, Richer JK, Takimoto GS, Tung L. Nuclear receptor coactivators and corepressors. Mol Endocrinol. 1996;10:1167–1177. - PubMed
-
- McKenna NJ, Lanz RB, O’Malley BW. Nuclear receptor coregulators: cellular and molecular biology. Endocr Rev. 1999;20:321–344. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

