Effect of apolipoprotein E on biomarkers of amyloid load and neuronal pathology in Alzheimer disease
- PMID: 20373342
- PMCID: PMC2886799
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.21953
Effect of apolipoprotein E on biomarkers of amyloid load and neuronal pathology in Alzheimer disease
Abstract
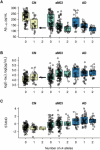
Objective: To study the effect of apolipoprotein E epsilon4 status on biomarkers of neurodegeneration (atrophy on magnetic resonance imaging [MRI]), neuronal injury (cerebrospinal fluid [CSF] t-tau), and brain Abeta amyloid load (CSF Abeta(1-42)) in cognitively normal subjects (CN), amnestic subjects with mild cognitive impairment (aMCI), and patients with Alzheimer disease (AD).
Methods: We included all 399 subjects (109 CN, 192 aMCI, 98 AD) from the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative study with baseline CSF and MRI scans. Structural Abnormality Index (STAND) scores, which reflect the degree of AD-like anatomic features on MRI, were computed for each subject.
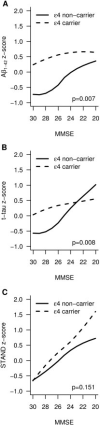
Results: A clear epsilon4 allele dose effect was seen on CSF Abeta(1-42) levels within each clinical group. In addition, the proportion of the variability in Abeta(1-42) levels explained by APOE epsilon4 dose was significantly greater than the proportion of the variability explained by clinical diagnosis. On the other hand, the proportion of the variability in CSF t-tau and MRI atrophy explained by clinical diagnosis was greater than the proportion of the variability explained by APOE epsilon4 dose; however, this effect was only significant for STAND scores.
Interpretation: Low CSF Abeta(1-42) (surrogate for Abeta amyloid load) is more closely linked to the presence of APOE epsilon4 than to clinical status. In contrast, MRI atrophy (surrogate for neurodegeneration) is closely linked with cognitive impairment, whereas its association with APOE epsilon4 is weaker. The data in this paper support a model of AD in which CSF Abeta(1-42) is the earliest of the 3 biomarkers examined to become abnormal in both APOE carriers and noncarriers.
Figures
Comment in
-
Beyond diagnosis: what biomarkers are teaching us about the "bio"logy of Alzheimer disease.Ann Neurol. 2010 Mar;67(3):283-5. doi: 10.1002/ana.22020. Ann Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20373338 No abstract available.
References
-
- Corder EH, Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ, et al. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in late onset families. Science. 1993;261:921–923. - PubMed
-
- Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ, Schmechel D, et al. Association of apolipoprotein E allele epsilon 4 with late-onset familial and sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1993;43:1467–1472. - PubMed
-
- Mayeux R, Stern Y, Ottman R, et al. The apolipoprotein epsilon 4 allele in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1993;34:752–754. - PubMed
-
- Tapiola T, Alafuzoff I, Herukka SK, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid {beta}-amyloid 42 and tau proteins as biomarkers of Alzheimer-type pathologic changes in the brain. Arch Neurol. 2009;66:382–389. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

