Cognition, reserve, and amyloid deposition in normal aging
- PMID: 20373347
- PMCID: PMC3074985
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.21904
Cognition, reserve, and amyloid deposition in normal aging
Abstract
Objective: To determine whether amyloid deposition is associated with impaired neuropsychological (NP) performance and whether cognitive reserve (CR) modifies this association.
Methods: In 66 normal elderly controls and 17 patients with Alzheimer disease (AD), we related brain retention of Pittsburgh Compound B (PiB) to NP performance and evaluated the impact of CR using education and American National Adult Reading Test intelligence quotient as proposed proxies.
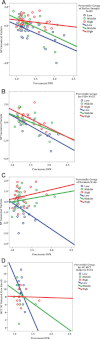
Results: We found in the combined sample of subjects that PiB retention in the precuneus was inversely related to NP performance, especially in tests of memory function, but also in tests of working memory, semantic processing, language, and visuospatial perception. CR significantly modified the relationship, such that at progressively higher levels of CR, increased amyloid deposition was less or not at all associated with poorer neuropsychological performance. In a subsample of normal controls, both the main effect of amyloid deposition of worse memory performance and the interaction with CR were replicated using a particularly challenging memory test.
Interpretation: Amyloid deposition is associated with lower cognitive performance both in AD patients and in the normal elderly, but the association is modified by CR, suggesting that CR may be protective against amyloid-related cognitive impairment.
Figures
References
-
- Arriagada PV, Growdon JH, Hedley-White ET, et al. Neurofibrillary tangles but not senile plaques parallel duration and severity of Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1992;42:631–639. - PubMed
-
- Arriagada PV, Marzloff K, Hyman BT. Distribution of Alzheimer-type pathologic changes in nondemented elderly individuals matches the pattern in Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1992;42:1681–1688. - PubMed
-
- Duyckaerts C, Colle MA, Dessi F, et al. Progression of Alzheimer histopathological changes. Acta Neurol Belg. 1998;98:180–185. - PubMed
-
- Giannakopoulos P, Herrmann FR, Bussiere T, et al. Tangle and neuron numbers, but not amyloid load, predict cognitive status in Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 2003;60:1495–1500. - PubMed
-
- Ingelsson M, Fukumoto H, Newell KL, et al. Early Abeta accumulation and progressive synaptic loss, gliosis, and tangle formation in AD brain. Neurology. 2004;62:925–931. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

