Accelerated slice encoding for metal artifact correction
- PMID: 20373445
- PMCID: PMC2894155
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.22112
Accelerated slice encoding for metal artifact correction
Abstract
Purpose: To demonstrate accelerated imaging with both artifact reduction and different contrast mechanisms near metallic implants.
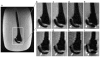
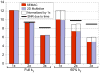
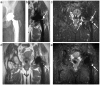
Materials and methods: Slice-encoding for metal artifact correction (SEMAC) is a modified spin echo sequence that uses view-angle tilting and slice-direction phase encoding to correct both in-plane and through-plane artifacts. Standard spin echo trains and short-TI inversion recovery (STIR) allow efficient PD-weighted imaging with optional fat suppression. A completely linear reconstruction allows incorporation of parallel imaging and partial Fourier imaging. The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) effects of all reconstructions were quantified in one subject. Ten subjects with different metallic implants were scanned using SEMAC protocols, all with scan times below 11 minutes, as well as with standard spin echo methods.
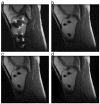
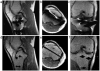
Results: The SNR using standard acceleration techniques is unaffected by the linear SEMAC reconstruction. In all cases with implants, accelerated SEMAC significantly reduced artifacts compared with standard imaging techniques, with no additional artifacts from acceleration techniques. The use of different contrast mechanisms allowed differentiation of fluid from other structures in several subjects.
Conclusion: SEMAC imaging can be combined with standard echo-train imaging, parallel imaging, partial-Fourier imaging, and inversion recovery techniques to offer flexible image contrast with a dramatic reduction of metal-induced artifacts in scan times under 11 minutes.
(c) 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Schenck JF. The role of magnetic susceptibility in magnetic resonance imaging: MRI magnetic compatibility of the first and second kinds. Med Phys. 1996;23:815–850. - PubMed
-
- Cho ZH, Ahn CB, Kim JH, Lee YE, Mun CW. Proc., SMRM, 6th Annual Meeting. New York: 1987. Phase error corrected interlaced echo planar imaging; p. 912.
-
- Chang H, Fitzpatrick J. A technique for accurate magnetic resonance imaging in the presence of field inhomogeneities. IEEE Transactions on medical imaging. 1992;11:319–329. - PubMed
-
- Hoff M, Xiang Q. Proceedings of the 17th Annual Meeting of ISMRM. Honolulu: 2009. Eliminating metal artifact distortion using 3d-place; p. 570.
-
- Olsen RV, Munk PL, Lee MJ, et al. Metal artifact reduction sequence: early clinical applications. Radiographics. 2000;20:699–712. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

