Evaluation of the Target Inhalation Mode (TIM) breathing maneuver in simulated nebulizer therapy in patients with cystic fibrosis
- PMID: 20373907
- PMCID: PMC3116626
- DOI: 10.1089/jamp.2009.0768
Evaluation of the Target Inhalation Mode (TIM) breathing maneuver in simulated nebulizer therapy in patients with cystic fibrosis
Abstract
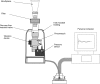
Background: Adaptive Aerosol Delivery (AAD) systems provide efficient drug delivery and improved lung deposition over conventional nebulizers by combining real-time analyses of patient breathing patterns and precisely timed aerosol delivery. Delivery and deposition are further enhanced by breathing techniques involving slow, deep inhalations.
Methods: This exploratory study assessed the acceptability of slow, deep inhalations in 20 patients with cystic fibrosis (CF) during up to eight simulated nebulizer treatments with the I-neb AAD System. The breathing maneuver, Target Inhalation Mode (TIM) breathing, involved the lengthening of the patient's inhalation time over successive breaths with guidance from auditory and tactile (vibratory) feedback from the device.
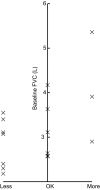
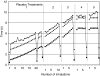
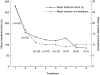
Results: At the end of the first treatment, most patients felt that the instructions were easy to understand (90%) and that the vibratory feedback was pleasant (65%). Half of the patients found the procedure to be comfortable. At the end of the final treatment, most patients felt that the breathing maneuver was easy to understand (90%) and use (80%), but that the duration of the breath was too long (100%). Logged data revealed that 90% of patients were able to comply with the breathing maneuver. The two patients unable to comply had a forced vital capacity of <1.75 L. The average treatment time decreased from 288.4 to 141.6 sec during the first and final treatments, respectively.
Conclusions: This study provides preliminary evidence of the acceptability of the TIM breathing maneuver in patients with CF and their ability to perform repeated TIM breathing during simulated nebulizer therapy with the I-neb AAD System.
Figures
References
-
- Lewis PA. The epidemiology of cystic fibrosis. In: Hodson ME, editor; Geddes DM, editor. Cystic Fibrosis. Chapman and Hall; London: 1995. pp. 1–13.
-
- Sheppard MN. The pathology of cystic fibrosis. In: Hodson ME, editor; Geddes DM, editor. Cystic Fibrosis. Chapman and Hall; London: 1995. pp. 131–149.
-
- Geller DE. Choosing a nebulizer for cystic fibrosis applications. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 1997;3:414–419. - PubMed
-
- Geller DE. Eigen H. Fiel SB. Clark A. Lamarre AP. Johnson CA. Konstan MW. Effect of smaller droplet size of dornase alfa on lung function in mild cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1998;25:83–87. - PubMed
-
- Le Brun PPH. de Boer AH. Gjaltema D. Hagedoorn P. Heijerman HGM. Frijlink HW. Inhalation of tobramycin in cystic fibrosis. Part 1: the choice of a nebulizer. Int J Pharm. 1999;189:205–214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

