Mode of breathing-tidal or slow and deep-through the I-neb Adaptive Aerosol Delivery (AAD) system affects lung deposition of (99m)Tc-DTPA
- PMID: 20373908
- PMCID: PMC3116638
- DOI: 10.1089/jamp.2009.0786
Mode of breathing-tidal or slow and deep-through the I-neb Adaptive Aerosol Delivery (AAD) system affects lung deposition of (99m)Tc-DTPA
Abstract
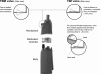
Background: The I-neb AAD System was designed to deliver aerosol with two different breathing pattern algorithms: the Tidal Breathing Mode (TBM) and the Target Inhalation Mode (TIM). For the purpose of the study, the TBM breathing pattern algorithm was set to guide the subjects to inhalation during tidal breathing with aerosol pulsed during 50-80% of the time spent on inhalation, whereas the TIM breathing pattern was set to guide the subject to a slow and deep inhalation of up to approximately 9 sec with aerosol pulsed for up to 7 sec, leaving 2 sec for particle deposition in the lungs. In TIM, the inspiratory flow was guided to approximately 20 L/min through a built-in resistance in the mouthpiece.
Methods: We have, in a randomized, open-label, crossover study of 12 healthy subjects evaluated lung deposition following administration of a radiolabeled aerosol from the I-neb AAD System with the TBM and TIM breathing patterns.
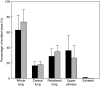
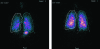
Results: The results showed that mean lung deposition was significantly higher when using the I-neb AAD System with the TIM breathing pattern (73.3%) than with the TBM breathing pattern (62.8%). The mean exhaled fractions were low (<1%) for both breathing patterns. The nebulization time was significantly shorter with the TIM breathing pattern (3.0 min) than with the TBM breathing pattern (4.7 min).
Conclusions: The results of the present study showed that lung deposition with the slow and deep inhalation achieved through the I-neb AAD System in TIM was superior to the lung deposition achieved during tidal breathing in TBM. With the combination of high lung deposition, almost no loss of aerosol during exhalation, and short nebulization time the I-neb AAD System with the TIM breathing pattern should be of special value to patients who require multiple daily dosing of aerosolized medication, are using drugs that should not be wasted into the room air, or would benefit from a more efficient delivery system.
Figures
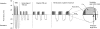
Similar articles
-
The I-neb Adaptive Aerosol Delivery System enhances delivery of alpha1-antitrypsin with controlled inhalation.J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2010 Apr;23 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S55-9. doi: 10.1089/jamp.2009.0793. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2010. PMID: 20373910 Free PMC article.
-
Lung Deposition of Alpha1-Proteinase Inhibitor (Human) (A1-PI[H]) Inhalation Solution Using Two Inhalation Modes of the I-neb Adaptive Aerosol Delivery (AAD) System in Healthy Subjects and Subjects with Cystic Fibrosis.J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2016 Jun;29(3):242-50. doi: 10.1089/jamp.2014.1173. Epub 2015 Dec 15. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2016. PMID: 26669827 Clinical Trial.
-
Domiciliary experience of the Target Inhalation Mode (TIM) breathing maneuver in patients with cystic fibrosis.J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2010 Apr;23 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S45-54. doi: 10.1089/jamp.2009.0777. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2010. PMID: 20373909 Free PMC article.
-
The Adaptive Aerosol Delivery (AAD) technology: Past, present, and future.J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2010 Apr;23 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S1-10. doi: 10.1089/jamp.2009.0791. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2010. PMID: 20373904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro characterization of the I-neb Adaptive Aerosol Delivery (AAD) system.J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2010 Apr;23 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S11-20. doi: 10.1089/jamp.2009.0792. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2010. PMID: 20373905 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting aerosol deposition to and within the lung airways using excipient enhanced growth.J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2013 Oct;26(5):248-65. doi: 10.1089/jamp.2012.0997. Epub 2013 Jan 3. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2013. PMID: 23286828 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Small Airways with Inhaled Corticosteroid/Long-Acting Beta Agonist Dry Powder Inhalers: A Functional Respiratory Imaging Study.J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2021 Sep;34(5):280-292. doi: 10.1089/jamp.2020.1618. Epub 2021 Apr 28. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2021. PMID: 33944614 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of airway disease on the deposition of inhaled drugs.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2024 Aug;21(8):1175-1190. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2024.2392790. Epub 2024 Aug 19. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2024. PMID: 39136493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regional Ventilation Is the Main Determinant of Alveolar Deposition of Coarse Particles in the Supine Healthy Human Lung During Tidal Breathing.J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2017 Oct;30(5):322-331. doi: 10.1089/jamp.2016.1336. Epub 2017 Mar 9. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2017. PMID: 28277885 Free PMC article.
-
Airway Deposition of Extrafine Inhaled Triple Therapy in Patients with COPD: A Model Approach Based on Functional Respiratory Imaging Computer Simulations.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2020 Oct 7;15:2433-2440. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S269001. eCollection 2020. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2020. PMID: 33116458 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson PJ. History of aerosol therapy: liquid nebulization to MDIs and DPIs. Resp Care. 2005;50:1139–1149. - PubMed
-
- Nikander K. Adaptive aerosol delivery: the principles. Eur Respir Rev. 1997:385–387.
-
- Denyer J. Adaptive aerosol delivery in practice. Eur Respir Rev. 1997:388–389.
-
- Denyer J. Nikander K. Smith NJ. Adaptive Aerosol Delivery (AAD) technology. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2004;1:165–176. - PubMed
-
- Nikander K. Denyer J. Adaptive Aerosol Delivery (AAD®) technology. In: Rathbone MJ, editor. Modified Release Drug Delivery Technology. 2nd. Informa Healthcare USA, Inc.; New York, NY: 2008. pp. 603–612.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

