Ketones prevent synaptic dysfunction induced by mitochondrial respiratory complex inhibitors
- PMID: 20374433
- PMCID: PMC3532617
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06728.x
Ketones prevent synaptic dysfunction induced by mitochondrial respiratory complex inhibitors
Abstract
Ketones have previously shown beneficial effects in models of neurodegenerative disorders, particularly against associated mitochondrial dysfunction and cognitive impairment. However, evidence of a synaptic protective effect of ketones remains lacking. We tested the effects of ketones on synaptic impairment induced by mitochondrial respiratory complex (MRC) inhibitors using electrophysiological, reactive oxygen species (ROS) imaging and biochemical techniques. MRC inhibitors dose-dependently suppressed both population spike (PS) and field potential amplitudes in the CA1 hippocampus. Pre-treatment with ketones strongly prevented changes in the PS, whereas partial protection was seen in the field potential. Rotenone (Rot; 100 nmol/L), a MRC I inhibitor, suppressed synaptic function without altering ROS levels and PS depression by Rot was unaffected by antioxidants. In contrast, antioxidant-induced PS recovery against the MRC II inhibitor 3-nitropropionic acid (3-NP; 1 mmol/L) was similar to the synaptic protective effects of ketones. Ketones also suppressed ROS generation induced by 3-NP. Finally, ketones reversed the decreases in ATP levels caused by Rot and 3-NP. In summary, our data demonstrate that ketones can preserve synaptic function in CA1 hippocampus induced by MRC dysfunction, likely through an antioxidant action and enhanced ATP generation.
Figures
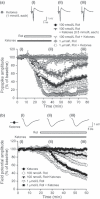
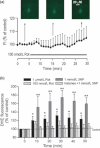
 ) Rot strongly depressed the PS amplitude during and after Rot application. Ketones alone
) Rot strongly depressed the PS amplitude during and after Rot application. Ketones alone  , Each 1 mmol/L) did not alter the PS amplitude. Pre-treatment with ketones fully reversed the synaptic suppression seen with 100 nmol/L Rot (
, Each 1 mmol/L) did not alter the PS amplitude. Pre-treatment with ketones fully reversed the synaptic suppression seen with 100 nmol/L Rot ( ), but this was partially restored with 1 μmol/L Rot (□). In each condition where 0.5 mmol/L ketones were tested against 100 nmol/L Rot (
), but this was partially restored with 1 μmol/L Rot (□). In each condition where 0.5 mmol/L ketones were tested against 100 nmol/L Rot ( ), ketones induced partial protective effects compared to 1 mmol/L ketones. (b) Changes in the mean field potential amplitude before, during, and after either 100 nmol/L or 1 μmol/L Rot with or without ketones. Rot slightly suppressed the field potential amplitude compared to the change in PS amplitude after Rot treatment. Both 100 nmol/L and 1 μmol/L Rot-induced field potentials were partially restored by ketone application. Representative traces of PS or field potentials at respective time-points (i, ii, iii) are depicted in the traces above. The horizontal line in this and following figures indicates the drug infusion period. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM.
), ketones induced partial protective effects compared to 1 mmol/L ketones. (b) Changes in the mean field potential amplitude before, during, and after either 100 nmol/L or 1 μmol/L Rot with or without ketones. Rot slightly suppressed the field potential amplitude compared to the change in PS amplitude after Rot treatment. Both 100 nmol/L and 1 μmol/L Rot-induced field potentials were partially restored by ketone application. Representative traces of PS or field potentials at respective time-points (i, ii, iii) are depicted in the traces above. The horizontal line in this and following figures indicates the drug infusion period. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM.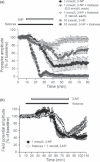
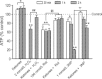
 ) irreversibly suppressed the PS amplitude in CA1 hippocampus. Pre-treatment with ketones did not produce a synaptic protective effect against 10 mmol/L 3-NP (
) irreversibly suppressed the PS amplitude in CA1 hippocampus. Pre-treatment with ketones did not produce a synaptic protective effect against 10 mmol/L 3-NP ( ), whereas ketones significantly reduced PS suppression induced by 1 mmol/L 3-NP (
), whereas ketones significantly reduced PS suppression induced by 1 mmol/L 3-NP ( ), and then restored the PS amplitude to basal levels after a 20-min washout. Lower concentrations of ketones (0.5 mmol/L each) were partially protective (
), and then restored the PS amplitude to basal levels after a 20-min washout. Lower concentrations of ketones (0.5 mmol/L each) were partially protective ( ). (b) During the initial period of 1 mmol/L 3-NP treatment (○), the mean field potential amplitude was slightly increased. After 30 min, the field potential showed dramatic decay and then did not change during wash-out. While pre-treatment with ketones slowly decreased the field potential amplitude compared to 1 mmol/L 3-NP alone, no beneficial effect occurred after 60 min of co-application. However, ketones significantly enhanced the recovery of the field potential amplitude after wash-out.
). (b) During the initial period of 1 mmol/L 3-NP treatment (○), the mean field potential amplitude was slightly increased. After 30 min, the field potential showed dramatic decay and then did not change during wash-out. While pre-treatment with ketones slowly decreased the field potential amplitude compared to 1 mmol/L 3-NP alone, no beneficial effect occurred after 60 min of co-application. However, ketones significantly enhanced the recovery of the field potential amplitude after wash-out.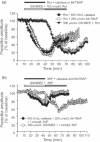
 ) alone also had no effect on Rot-induced PS suppression. (b) Co-application of a cocktail of 600 U/mL catalase and 200 μmol/L MnTBAP with 1 mmol/L 3-NP resulted in recovery of the PS amplitude. Similarly, pre-treatment with GSHMEE also restored the PS amplitude against 3-NP application.
) alone also had no effect on Rot-induced PS suppression. (b) Co-application of a cocktail of 600 U/mL catalase and 200 μmol/L MnTBAP with 1 mmol/L 3-NP resulted in recovery of the PS amplitude. Similarly, pre-treatment with GSHMEE also restored the PS amplitude against 3-NP application.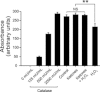
Similar articles
-
Acute exposure to the mitochondrial complex I toxin rotenone impairs synaptic long-term potentiation in rat hippocampal slices.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012 Aug;18(8):641-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2012.00337.x. Epub 2012 May 22. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012. PMID: 22613619 Free PMC article.
-
Ketones prevent oxidative impairment of hippocampal synaptic integrity through KATP channels.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 7;10(4):e0119316. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119316. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25848768 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective efficacy of naringin on 3-nitropropionic acid-induced mitochondrial dysfunction through the modulation of Nrf2 signaling pathway in PC12 cells.Mol Cell Biochem. 2015 Nov;409(1-2):199-211. doi: 10.1007/s11010-015-2525-9. Epub 2015 Aug 18. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015. PMID: 26280522
-
Possible neuroprotective effect of Withania somnifera root extract against 3-nitropropionic acid-induced behavioral, biochemical, and mitochondrial dysfunction in an animal model of Huntington's disease.J Med Food. 2009 Jun;12(3):591-600. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2008.0028. J Med Food. 2009. PMID: 19627208
-
Mitochondrial toxins and neurodegenerative diseases.Front Biosci. 2007 Jan 1;12:986-1007. doi: 10.2741/2119. Front Biosci. 2007. PMID: 17127354 Review.
Cited by
-
Ketogenic Diet: An Effective Treatment Approach for Neurodegenerative Diseases.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022 Nov 15;20(12):2303-2319. doi: 10.2174/1570159X20666220830102628. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36043794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ketone body therapy: from the ketogenic diet to the oral administration of ketone ester.J Lipid Res. 2014 Sep;55(9):1818-26. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R046599. Epub 2014 Mar 5. J Lipid Res. 2014. PMID: 24598140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Altered Skeletal Muscle Mitochondrial Proteome As the Basis of Disruption of Mitochondrial Function in Diabetic Mice.Diabetes. 2016 Mar;65(3):561-73. doi: 10.2337/db15-0823. Epub 2015 Dec 30. Diabetes. 2016. PMID: 26718503 Free PMC article.
-
The metabolic basis of epilepsy.Nat Rev Neurol. 2022 Jun;18(6):333-347. doi: 10.1038/s41582-022-00651-8. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Nat Rev Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35361967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Ketogenic Diet Improves Cognition and Has Biochemical Effects in Prefrontal Cortex That Are Dissociable From Hippocampus.Front Aging Neurosci. 2018 Dec 3;10:391. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2018.00391. eCollection 2018. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30559660 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexi T, Hughes PE, Faull RL, Williams CE. 3-Nitropropionic acid’s lethal triplet: cooperative pathways of neurodegeneration. Neuroreport. 1998;9:R57–R64. - PubMed
-
- Avshalumov MV, Chen BT, Rice ME. Mechanisms underlying H(2)O(2)-mediated inhibition of synaptic transmission in rat hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 2000;882:86–94. - PubMed
-
- Ayala A, Venero JL, Cano J, Machado A. Mitochondrial toxins and neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Biosci. 2007;12:986–1007. - PubMed
-
- Balietti M, Giorgetti B, Fattoretti P, et al. Ketogenic diets cause opposing changes in synaptic morphology in CA1 hippocampus and dentate gyrus of late-adult rats. Rejuvenation Res. 2008;11:631–640. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

