Microvascular responses to cardiovascular risk factors
- PMID: 20374483
- PMCID: PMC3071571
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1549-8719.2009.00015.x
Microvascular responses to cardiovascular risk factors
Abstract
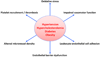
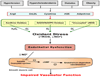
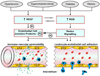
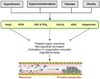
Hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, diabetes, and obesity are among a growing list of conditions that have been designated as major risk factors for cardiovascular disease (CVD). While CVD risk factors are well known to enhance the development of atherosclerotic lesions in large arteries, there is also evidence that the structure and function of microscopic blood vessels can be profoundly altered by these conditions. The diverse responses of the microvasculature to CVD risk factors include oxidative stress, enhanced leukocyte- and platelet-endothelial cell adhesion, impaired endothelial barrier function, altered capillary proliferation, enhanced thrombosis, and vasomotor dysfunction. Emerging evidence indicates that a low-grade systemic inflammatory response that results from risk factor-induced cell activation and cell-cell interactions may underlie the phenotypic changes induced by risk factor exposure. A consequence of the altered microvascular phenotype and systemic inflammatory response is an enhanced vulnerability of tissues to the deleterious effects of secondary oxidative and inflammatory stresses, such as ischemia and reperfusion. Future efforts to develop therapies that prevent the harmful effects of risk factor-induced inflammation should focus on the microcirculation.
Figures
References
-
- Allen CL, Bayraktutan U. Antioxidants attenuate hyperglycaemia-mediated brain endothelial cell dysfunction and blood-brain barrier hyperpermeability. Diabetes Obesity Metab. 2009;11:480–490. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez A, Sanz MJ. Reactive oxygen species mediate angiotensin II-induced leukocyte-endothelial cell interactions in vivo. J Leukoc Biol. 2001;70:199–206. - PubMed
-
- Anfossi G, Russo I, Trovati M. Platelet dysfunction in central obesity. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2009;19:440–449. - PubMed
-
- Bagi Z, Feher A, Beleznai T. Preserved coronary arteriolar dilatation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Implications for reactive oxygen species. Pharmacological Reports. 2009;61:99–104. - PubMed
-
- Balakumar P, Singh H, Singh M, Anand-Srivastava MB. The impairment of preconditioning-mediated cardioprotection in pathological conditions. Pharmacol Res. 2009;60:18–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

