Discrimination of different species from the genus Drosophila by intact protein profiling using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry
- PMID: 20374617
- PMCID: PMC2858148
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2148-10-95
Discrimination of different species from the genus Drosophila by intact protein profiling using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry
Abstract
Background: The use of molecular biology-based methods for species identification and establishing phylogenetic relationships has supplanted traditional methods relying on morphological characteristics. While PCR-based methods are now the commonly accepted gold standards for these types of analysis, relatively high costs, time-consuming assay development or the need for a priori information about species-specific sequences constitute major limitations. In the present study, we explored the possibility to differentiate between 13 different species from the genus Drosophila via a molecular proteomic approach.
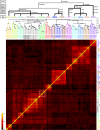
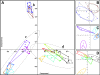
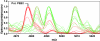
Results: After establishing a simple protein extraction procedure and performing matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometry (MS) with intact proteins and peptides, we could show that most of the species investigated reproducibly yielded mass spectra that were adequate for species classification. Furthermore, a dendrogram generated by cluster analysis of total protein patterns agrees reasonably well with established phylogenetic relationships.
Conclusion: Considering the intra- and interspecies similarities and differences between spectra obtained for specimens of closely related Drosophila species, we estimate that species typing of insects and possibly other multicellular organisms by intact protein profiling (IPP) can be established successfully for species that diverged from a common ancestor about 3 million years ago.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Species determination of Culicoides biting midges via peptide profiling using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry.Parasit Vectors. 2014 Aug 24;7:392. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-7-392. Parasit Vectors. 2014. PMID: 25152308 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosomal subunit protein typing using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) for the identification and discrimination of Aspergillus species.BMC Microbiol. 2017 Apr 26;17(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s12866-017-1009-3. BMC Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28441930 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic profiling of intact mycobacteria by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry.Anal Chem. 2004 Oct 1;76(19):5769-76. doi: 10.1021/ac049410m. Anal Chem. 2004. PMID: 15456297
-
Differentiation and authentication of fishes at the species level through analysis of fish skin by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2019 Aug 30;33(16):1336-1343. doi: 10.1002/rcm.8474. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2019. PMID: 31034697
-
Rapid Identification of the Foodborne Pathogen Trichinella spp. by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 21;11(3):e0152062. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152062. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26999436 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Detection of Alphitobius diaperinus by Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction With a Single-Copy Gene Target.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Mar 9;9:718806. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.718806. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35356786 Free PMC article.
-
MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry: an emerging technology for microbial identification and diagnosis.Front Microbiol. 2015 Aug 5;6:791. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00791. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26300860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of European mosquito species by MALDI-TOF MS.Parasitol Res. 2014 Jun;113(6):2375-8. doi: 10.1007/s00436-014-3876-y. Epub 2014 Apr 16. Parasitol Res. 2014. PMID: 24737398
-
MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry detection of pathogens in vectors: the Borrelia crocidurae/Ornithodoros sonrai paradigm.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014 Jul 24;8(7):e2984. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002984. eCollection 2014 Jul. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014. PMID: 25058611 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Algerian Field-Caught Phlebotomine Sand Fly Vectors by MALDI-TOF MS.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016 Jan 15;10(1):e0004351. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004351. eCollection 2016 Jan. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016. PMID: 26771833 Free PMC article.
References
-
- The Barcode of Life Initiative. http://www.barcoding.si.edu
-
- Folmer O, Black M, Hoeh W, Lutz R, Vrijenhoek R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol Mar Biol Biotechnol. 1994;3:294–9. - PubMed
-
- Holland RD, Wilkes JG, Rafii F, Sutherland JB, Persons CC, Voorhees KJ, Lay JO Jr. Rapid identification of intact whole bacteria based on spectral patterns using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization with time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 1996;10:1227–32. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0231(19960731)10:10<1227::AID-RCM659>3.0.CO;2-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

