Early administration of IL-6RA does not prevent radiation-induced lung injury in mice
- PMID: 20374625
- PMCID: PMC2864283
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-5-26
Early administration of IL-6RA does not prevent radiation-induced lung injury in mice
Abstract
Background: Radiation pneumonia and subsequent radiation lung fibrosis are major dose-limiting complications for patients undergoing thoracic radiotherapy. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a pleiotropic cytokine and plays important roles in the regulation of immune response and inflammation. The purpose of this study was to investigate whether anti-IL-6 monoclonal receptor antibody (IL-6RA) could ameliorate radiation-induced lung injury in mice.
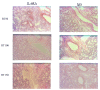
Methods: BALB/cAnNCrj mice having received thoracic irradiation of 21 Gy were injected intraperitoneally with IL-6RA (MR16-1) or control rat IgG twice, immediately and seven days after irradiation. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to examine the plasma level of IL-6 and serum amyloid A (SAA). Lung injury was assessed by histological staining with haematoxylin and eosin or Azan, measuring lung weight, and hydroxyproline.
Results: The mice treated with IL-6RA did not survive significantly longer than the rat IgG control. We observed marked up-regulation of IL-6 in mice treated with IL-6RA 150 days after irradiation, whereas IL-6RA temporarily suppressed early radiation-induced increase in the IL-6 release level. Histopathologic assessment showed no differences in lung section or lung weight between mice treated with IL-6RA and control.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that early treatment with IL-6RA after irradiation alone does not protect against radiation-induced lung injury.
Figures
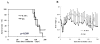
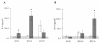
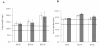

Similar articles
-
Anti-IL-6 receptor antibody does not ameliorate radiation pneumonia in mice.Exp Ther Med. 2012 Aug;4(2):273-276. doi: 10.3892/etm.2012.582. Epub 2012 May 18. Exp Ther Med. 2012. PMID: 22984368 Free PMC article.
-
The chemokine, CCL3, and its receptor, CCR1, mediate thoracic radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011 Jul;45(1):127-35. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2010-0265OC. Epub 2010 Sep 24. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 20870892 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of lipopolysaccharide on the response of C57BL/6J mice to whole thorax irradiation.Radiother Oncol. 2012 Dec;105(3):341-9. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2012.08.003. Epub 2012 Sep 14. Radiother Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22985778 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of radiation-induced pneumonitis by recombinant adenovirus-mediated transferring of soluble TGF-beta type II receptor gene.Cancer Gene Ther. 2006 Sep;13(9):864-72. doi: 10.1038/sj.cgt.7700959. Epub 2006 May 19. Cancer Gene Ther. 2006. PMID: 16710346
-
Radiation and the lung: a reevaluation of the mechanisms mediating pulmonary injury.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995 Jan 15;31(2):361-9. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(94)00477-3. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995. PMID: 7836090 Review.
Cited by
-
Protective effect of ulinastatin in patients with non-small cell lung cancer after radiation therapy: a randomized, placebo-controlled study.Med Oncol. 2015 Jan;32(1):405. doi: 10.1007/s12032-014-0405-x. Epub 2014 Dec 12. Med Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25502081 Clinical Trial.
-
Serum Amyloid A as a Biomarker for Radiation Exposure.Radiat Res. 2015 Jul;184(1):14-23. doi: 10.1667/RR13927.1. Epub 2015 Jun 26. Radiat Res. 2015. PMID: 26114330 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-IL-6 receptor antibody does not ameliorate radiation pneumonia in mice.Exp Ther Med. 2012 Aug;4(2):273-276. doi: 10.3892/etm.2012.582. Epub 2012 May 18. Exp Ther Med. 2012. PMID: 22984368 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Metabolomics and Transcriptomics Approaches to Assess the IL-6 Blockade as a Therapeutic of ALS: Deleterious Alteration of Lipid Metabolism.Neurotherapeutics. 2016 Oct;13(4):905-917. doi: 10.1007/s13311-016-0461-3. Neurotherapeutics. 2016. PMID: 27444617 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokines and radiation-induced pulmonary injuries.J Radiat Res. 2018 Nov 1;59(6):709-753. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rry067. J Radiat Res. 2018. PMID: 30169853 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mehta V. Radiation pneumonitis and pulmonary fibrosis in non-small-cell lung cancer: pulmonary function, prediction, and prevention. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005;63:5–24. - PubMed
-
- Yu TK, Whitman GJ, Thames HD, Buzdar AU, Strom EA, Perkins GH, Schechter NR, McNeese MD, Kau SW, Thomas ES, Hortobagyi GN, Buchholz TA. Clinically relevant pneumonitis after sequential paclitaxel-based chemotherapy and radiotherapy in breast cancer patients. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004;96:1676–1681. - PubMed
-
- Tsoutsou PG, Koukourakis MI. Radiation pneumonitis and fibrosis: mechanisms underlying its pathogenesis and implications for future research. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;66:1281–1293. - PubMed
-
- Rubin P, Johnston CJ, Williams JP, McDonald S, Finkelstein JN. A perpetual cascade of cytokines postirradiation leads to pulmonary fibrosis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995;33:99–109. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

