Direct insulin and leptin action on pro-opiomelanocortin neurons is required for normal glucose homeostasis and fertility
- PMID: 20374961
- PMCID: PMC2854520
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2010.03.002
Direct insulin and leptin action on pro-opiomelanocortin neurons is required for normal glucose homeostasis and fertility
Abstract
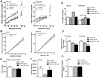
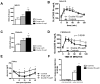
Circulating leptin and insulin convey information regarding energy stores to the central nervous system, particularly the hypothalamus. Hypothalamic pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) neurons regulate energy balance and glucose homeostasis and express leptin and insulin receptors. However, the physiological significance of concomitant leptin and insulin action on POMC neurons remains to be established. Here, we show that mice lacking both leptin and insulin receptors in POMC neurons (Pomc-Cre, Lepr(flox/flox) IR(flox/flox) mice) display systemic insulin resistance, which is distinct from the single deletion of either receptor. In addition, Pomc-Cre, Lepr(flox/flox) IR(flox/flox) female mice display elevated serum testosterone levels and ovarian abnormalities, resulting in reduced fertility. We conclude that direct action of insulin and leptin on POMC neurons is required to maintain normal glucose homeostasis and reproductive function.
2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Accili D, Arden KC. FoxOs at the crossroads of cellular metabolism, differentiation, and transformation. Cell. 2004;117:421–426. - PubMed
-
- Adashi EY, Hsueh AJ, Yen SS. Insulin enhancement of luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone release by cultured pituitary cells. Endocrinology. 1981;108:1441–1449. - PubMed
-
- Balthasar N, Coppari R, McMinn J, Liu SM, Lee CE, Tang V, Kenny CD, McGovern RA, Chua SC, Jr, Elmquist JK, et al. Leptin receptor signaling in POMC neurons is required for normal body weight homeostasis. Neuron. 2004;42:983–991. - PubMed
-
- Barbieri RL, Makris A, Randall RW, Daniels G, Kistner RW, Ryan KJ. Insulin stimulates androgen accumulation in incubations of ovarian stroma obtained from women with hyperandrogenism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986;62:904–910. - PubMed
-
- Baskin D, Schwartz MW, Seeley RJ, Woods SC, Porte D, Jr, Breininger JF, Jonak Z, Schaefer J, Krouse M, Burghardt C, et al. Leptin receptor long-form splice-variant protein expression in neuron cell bodies of the brain and co-localization with neuropeptide Y mRNA in the arcuate nucleus. J Histochem Cytochem. 1999;47:353–362. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HD061539/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- RL1 DK081185/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK53301/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1UL1RR024923/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K99 DK085330/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK053301/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RL1DK081185/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- TL1DK081181/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK056116/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD028934/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54-HD28934/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 1F32DK066972/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HD056491/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK053301/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK56116/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK066972/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1PL1DK081182/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K99HD056491/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024923/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- PL1 DK081182/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

