The mobile FG nucleoporin Nup98 is a cofactor for Crm1-dependent protein export
- PMID: 20375145
- PMCID: PMC2877646
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e09-12-1041
The mobile FG nucleoporin Nup98 is a cofactor for Crm1-dependent protein export
Abstract
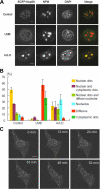
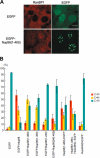
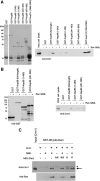
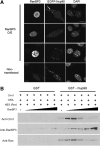
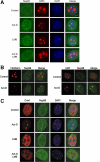
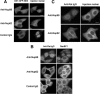
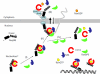
Nup98 is a mobile nucleoporin that forms distinct dots in the nucleus, and, although a role for Nup98 in nuclear transport has been suggested, its precise function remains unclear. Here, we show that Nup98 plays an important role in Crm1-mediated nuclear protein export. Nuclear, but not cytoplasmic, dots of EGFP-tagged Nup98 disappeared rapidly after cell treatment with leptomycin B, a specific inhibitor of the nuclear export receptor, Crm1. Mutational analysis demonstrated that Nup98 physically and functionally interacts with Crm1 in a RanGTP-dependent manner through its N-terminal phenylalanine-glycine (FG) repeat region. Moreover, the activity of the Nup98-Crm1 complex was modulated by RanBP3, a known cofactor for Crm1-mediated nuclear export. Finally, cytoplasmic microinjection of anti-Nup98 inhibited the Crm1-dependent nuclear export of proteins, concomitant with the accumulation of anti-Nup98 in the nucleus. These results clearly demonstrate that Nup98 functions as a novel shuttling cofactor for Crm1-mediated nuclear export in conjunction with RanBP3.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

