Regulation of de novo-initiated RNA synthesis in hepatitis C virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase by intermolecular interactions
- PMID: 20375156
- PMCID: PMC2876623
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02446-09
Regulation of de novo-initiated RNA synthesis in hepatitis C virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase by intermolecular interactions
Abstract
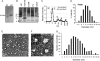
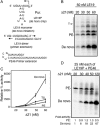
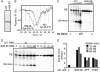
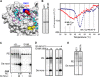
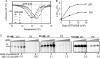
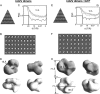
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) has been proposed to change conformations in association with RNA synthesis and to interact with cellular proteins. In vitro, the RdRp can initiate de novo from the ends of single-stranded RNA or extend a primed RNA template. The interactions between the Delta1 loop and thumb domain in NS5B are required for de novo initiation, although it is unclear whether these interactions are within an NS5B monomer or are part of a higher-order NS5B oligomeric complex. This work seeks to address how polymerase conformation and/or oligomerization affects de novo initiation. We have shown that an increasing enzyme concentration increases de novo initiation by the genotype 1b and 2a RdRps while primer extension reactions are not affected or inhibited under similar conditions. Initiation-defective mutants of the HCV polymerase can increase de novo initiation by the wild-type (WT) polymerase. GTP was also found to stimulate de novo initiation. Our results support a model in which the de novo initiation-competent conformation of the RdRp is stimulated by oligomeric contacts between individual subunits. Using electron microscopy and single-molecule reconstruction, we attempted to visualize the low-resolution conformations of a dimer of a de novo initiation-competent HCV RdRp.
Figures


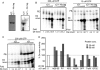

Similar articles
-
De novo initiation of RNA synthesis by the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (NS5B) of hepatitis C virus.J Virol. 2000 Jan;74(2):851-63. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.2.851-863.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10623748 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of hepatitis C virus RNA polymerases ser29 and ser42 by protein kinase C-related kinase 2 regulates viral RNA replication.J Virol. 2014 Oct;88(19):11240-52. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01826-14. Epub 2014 Jul 16. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 25031343 Free PMC article.
-
Functional characterization of fingers subdomain-specific monoclonal antibodies inhibiting the hepatitis C virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase.J Biol Chem. 2008 Aug 29;283(35):24089-102. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M803422200. Epub 2008 Jun 23. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18574240 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis C virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (NS5B polymerase).Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2000;242:225-60. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-59605-6_11. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10592663 Review. No abstract available.
-
Using the Hepatitis C Virus RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase as a Model to Understand Viral Polymerase Structure, Function and Dynamics.Viruses. 2015 Jul 17;7(7):3974-94. doi: 10.3390/v7072808. Viruses. 2015. PMID: 26193306 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Supramolecular arrangement of the full-length Zika virus NS5.PLoS Pathog. 2019 Apr 5;15(4):e1007656. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007656. eCollection 2019 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 30951555 Free PMC article.
-
Affinity labeling of hepatitis C virus replicase with a nucleotide analogue: identification of binding site.Biochemistry. 2013 Jan 15;52(2):432-44. doi: 10.1021/bi301098g. Epub 2013 Jan 4. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23268692 Free PMC article.
-
Purification and Biochemical Characterisation of Rabbit Calicivirus RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerases and Identification of Non-Nucleoside Inhibitors.Viruses. 2016 Apr 14;8(4):100. doi: 10.3390/v8040100. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27089358 Free PMC article.
-
Viral double-strand RNA-binding proteins can enhance innate immune signaling by toll-like Receptor 3.PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e25837. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025837. Epub 2011 Oct 10. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22016778 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and regulatory elements of HCV NS5B polymerase--β-loop and C-terminal tail--are required for activity of allosteric thumb site II inhibitors.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 9;9(1):e84808. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084808. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24416288 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahlquist, P., S. X. Wu, P. Kaesberg, C. C. Kao, R. Quadt, W. DeJong, and R. Hershberger. 1994. Protein-protein interactions and glycerophospholipids in bromovirus and nodavirus RNA replication. Arch. Virol. Suppl. 9:135-145. - PubMed
-
- Biswal, B. K., M. M. Cherney, M. Wang, L. Chan, C. G. Yannopoulos, D. Bilimoria, O. Nicolas, J. Bedard, and M. N. James. 2005. Crystal structures of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase genotype 2a of hepatitis C virus reveal two conformations and suggest mechanisms of inhibition by non-nucleoside inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 280:18202-18210. - PubMed
-
- Blumenthal, T., and G. G. Carmichael. 1979. RNA replication: function and structure of Qbeta-replicase. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 48:525-548. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

