Epidermal growth factor inhibits intestinal NHE8 expression via reducing its basal transcription
- PMID: 20375273
- PMCID: PMC2904261
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00081.2010
Epidermal growth factor inhibits intestinal NHE8 expression via reducing its basal transcription
Abstract
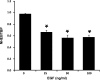
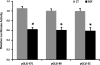
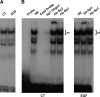
Sodium/hydrogen exchangers (NHEs) play a major role in Na(+) absorption, cell volume regulation, and intracellular pH regulation. Of the nine identified mammalian NHEs, three (NHE2, NHE3, and NHE8) are localized on the apical membrane of epithelial cells in the small intestine and the kidney. Although the regulation of NHE2 and NHE3 expression has been extensively studied in the past decade, little is known about the regulation of NHE8 gene expression under physiological conditions. The current studies were performed to explore the role of epidermal growth factor (EGF) on NHE8 expression during intestinal maturation. Brush-border membrane vesicles (BBMV) were isolated from intestinal epithelia, and Western blot analysis was performed to determine NHE8 protein expression of sucking male rats treated with EGF. Real-time PCR was used to quantitate NHE8 mRNA expression in rats and Caco-2 cells. Human NHE8 promoter activity was characterized through transfection of Caco-2 cells. Gel mobility shift assays (GMSAs) were used to identify the promoter sequences and the transcriptional factors involved in EGF-mediated regulation. Our results showed that intestinal NHE8 mRNA expression was decreased in EGF-treated rats and Caco-2 cells, and NHE8 protein abundance was also decreased in EGF-treated rats. The activity of the human NHE8 gene promoter transfected in Caco-2 cells was also reduced by EGF treatment. This could be explained by reduced binding of transcription factor Sp3 on the NHE8 basal promoter region in the presence of EGF. Pretreatment with MEK1/2 inhibitor UO-126 could prevent EGF-mediated inhibition of NHE8 gene expression. In conclusion, this study showed that EGF inhibits NHE8 gene expression through reducing its basal transcription, suggesting an important role of EGF in regulating NHE expression during intestinal maturation.
Figures
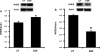



Similar articles
-
Transcriptional inhibition of intestinal NHE8 expression by glucocorticoids involves Pax5.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010 Oct;299(4):G921-7. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00227.2010. Epub 2010 Jul 29. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20671194 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor necrosis factor-{alpha} downregulates intestinal NHE8 expression by reducing basal promoter activity.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009 Mar;296(3):C489-97. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00482.2008. Epub 2008 Dec 24. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19109523 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal growth factor regulation of rat NHE2 gene expression.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2001 Aug;281(2):C504-13. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.2001.281.2.C504. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11443049
-
Transcriptional regulation of the intestinal luminal Na⁺ and Cl⁻ transporters.Biochem J. 2011 Apr 15;435(2):313-25. doi: 10.1042/BJ20102062. Biochem J. 2011. PMID: 21726200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Short-term regulation of NHE3 by EGF and protein kinase C but not protein kinase A involves vesicle trafficking in epithelial cells and fibroblasts.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;915:30-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb05221.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000. PMID: 11193592 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of pHi in Intestinal Epithelial Proliferation-Transport Mechanisms, Regulatory Pathways, and Consequences.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jan 22;9:618135. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.618135. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33553180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sodium butyrate stimulates NHE8 expression via its role on activating NHE8 basal promoter activity.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015 Sep 15;309(6):G500-5. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00194.2015. Epub 2015 Jul 9. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26159698 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal growth factor upregulates serotonin transporter in human intestinal epithelial cells via transcriptional mechanisms.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011 Apr;300(4):G627-36. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00563.2010. Epub 2011 Jan 27. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21273531 Free PMC article.
-
The Physiological Function and Potential Role of the Ubiquitous Na+/H+ Exchanger Isoform 8 (NHE8): An Overview Data.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 17;23(18):10857. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810857. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142772 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NHE8 plays an important role in mucosal protection via its effect on bacterial adhesion.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013 Jul 1;305(1):C121-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00101.2013. Epub 2013 May 8. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23657568 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amin MR, Malakooti J, Sandoval R, Dudeja PK, Ramaswamy K. IFN-γ and TNF-α regulate human NHE3 gene expression by modulating the Sp family transcription factors in human intestinal epithelial cell line C2BBe1. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 291: C887–C896, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Bai L, Collins JF, Muller YL, Xu H, Kiela PR, Ghishan FK. Characterization of cis-elements required for osmotic response of rat Na+/H+ exchanger-2 (NHE-2) gene. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 277: R1112–R1119, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Beardmore JM, Richards RC. Concentrations of epidermal growth factor in mouse milk throughout lactation. J Endocrinol 96: 287–292, 1983 - PubMed
-
- Bell SM, Schreiner CM, Schultheis PJ, Miller ML, Evans RL, Vorhees CV, Shull GE, Scott WJ. Targeted disruption of the murine NHE1 locus induces ataxia, growth retardation, and seizures. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 276: C788–C795, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Boivin GP, Schultheis PJ, Shull GE, Stemmermann GN. Variant form of diffuse corporal gastritis in NHE2 knockout mice. Comp Med 50: 511–515, 2000 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

