Deletion of the anion exchanger Slc26a4 (pendrin) decreases apical Cl(-)/HCO3(-) exchanger activity and impairs bicarbonate secretion in kidney collecting duct
- PMID: 20375274
- PMCID: PMC2904254
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00033.2010
Deletion of the anion exchanger Slc26a4 (pendrin) decreases apical Cl(-)/HCO3(-) exchanger activity and impairs bicarbonate secretion in kidney collecting duct
Abstract
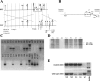
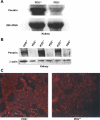
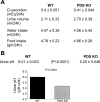
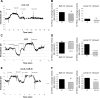
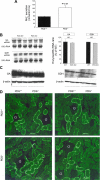
The anion exchanger Pendrin, which is encoded by SLC26A4 (human)/Slc26a4 (mouse) gene, is localized on the apical membrane of non-acid-secreting intercalated (IC) cells in the kidney cortical collecting duct (CCD). To examine its role in the mediation of bicarbonate secretion in vivo and the apical Cl(-)/HCO(3)(-) exchanger in the kidney CCD, mice with genetic deletion of pendrin were generated. The mutant mice show the complete absence of pendrin expression in their kidneys as assessed by Northern blot hybridization, Western blot, and immunofluorescence labeling. Pendrin knockout (KO) mice display significantly acidic urine at baseline [pH 5.20 in KO vs. 6.01 in wild type (WT); P < 0.0001] along with elevated serum HCO(3)(-) concentration (27.4 vs. 24 meq/l in KO vs. WT, respectively; P < 0.02), consistent with decreased bicarbonate secretion in vivo. The urine chloride excretion was comparable in WT and KO mice. For functional studies, CCDs were microperfused and IC cells were identified by their ability to trap the pH fluorescent dye BCECF. The apical Cl(-)/HCO(3)(-) exchanger activity in B-IC and non-A, non-B-IC cells, as assessed by intracellular pH monitoring, was significantly reduced in pendrin-null mice. The basolateral Cl(-)/HCO(3)(-) exchanger activity in A-IC cells and in non-A, non-B-IC cells, was not different in pendrin KO mice relative to WT animals. Urine NH(4)(+) (ammonium) excretion increased significantly, consistent with increased trapping of NH(3) in the collecting duct in pendrin KO mice. We conclude that Slc26a4 (pendrin) deletion impairs the secretion of bicarbonate in vivo and reduces apical Cl(-)/HCO(3)(-) exchanger activity in B-IC and non-A, non-B-IC cells in CCD. Additional apical Cl(-)/HCO(3)(-) exchanger(s) is (are) present in the CCD.
Figures
References
-
- Amlal H, Sheriff S, Faroqui S, Ma L, Barone S, Petrovic S, Soleimani M. Regulation of acid-base transporters by vasopressin in the kidney collecting duct of Brattleboro rat. Am J Nephrol 26: 194–205, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Atkins JL, Burg MB. Bicarbonate transport by isolated perfused rat collecting ducts. Am J Physiol Renal Fluid Electrolyte Physiol 249: F485–F489, 1985 - PubMed
-
- Bissig M, Hagenbuch B, Stieger B, Koller T, Meier PJ. Functional expression cloning of the canalicular sulfate transport system of rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem 269: 3017–3021, 1994 - PubMed
-
- Brown D, Breton S. H+V-ATPase-dependent luminal acidification in the kidney collecting duct and the epididymis/vas deferens: vesicle recycling and transcytotic pathways. J Exp Biol 203: 137–145, 2000 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

