Ceramide modulates HERG potassium channel gating by translocation into lipid rafts
- PMID: 20375276
- PMCID: PMC2904259
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00462.2009
Ceramide modulates HERG potassium channel gating by translocation into lipid rafts
Abstract
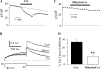
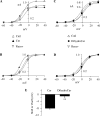
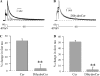
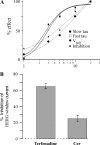
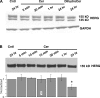
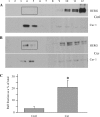
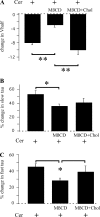
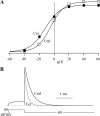
Human ether-à-go-go-related gene (HERG) potassium channels play an important role in cardiac action potential repolarization, and HERG dysfunction can cause cardiac arrhythmias. However, recent evidence suggests a role for HERG in the proliferation and progression of multiple types of cancers, making it an attractive target for cancer therapy. Ceramide is an important second messenger of the sphingolipid family, which due to its proapoptotic properties has shown promising results in animal models as an anticancer agent. Yet the acute effects of ceramide on HERG potassium channels are not known. In the present study we examined the effects of cell-permeable C(6)-ceramide on HERG potassium channels stably expressed in HEK-293 cells. C(6)-ceramide (10 microM) reversibly inhibited HERG channel current (I(HERG)) by 36 +/- 5%. Kinetically, ceramide induced a significant hyperpolarizing shift in the current-voltage relationship (DeltaV(1/2) = -8 +/- 0.5 mV) and increased the deactivation rate (43 +/- 3% for tau(fast) and 51 +/- 3% for tau(slow)). Mechanistically, ceramide recruited HERG channels within caveolin-enriched lipid rafts. Cholesterol depletion and repletion experiments and mathematical modeling studies confirmed that inhibition and gating effects are mediated by separate mechanisms. The ceramide-induced hyperpolarizing gating shift (raft mediated) could offset the impact of inhibition (raft independent) during cardiac action potential repolarization, so together they may nullify any negative impact on cardiac rhythm. Our results provide new insights into the effects of C(6)-ceramide on HERG channels and suggest that C(6)-ceramide can be a promising therapeutic for cancers that overexpress HERG.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sphingolipid metabolite ceramide causes metabolic perturbation contributing to HERG K+ channel dysfunction.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2007;20(5):429-40. doi: 10.1159/000107527. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17762170
-
State-dependent block of HERG potassium channels by R-roscovitine: implications for cancer therapy.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009 Apr;296(4):C701-10. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00633.2008. Epub 2009 Feb 25. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19244476 Free PMC article.
-
hERG potassium channel gating is mediated by N- and C-terminal region interactions.J Gen Physiol. 2011 Mar;137(3):315-25. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201010582. J Gen Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21357734 Free PMC article.
-
The cardiac hERG/IKr potassium channel as pharmacological target: structure, function, regulation, and clinical applications.Curr Pharm Des. 2006;12(18):2271-83. doi: 10.2174/138161206777585102. Curr Pharm Des. 2006. PMID: 16787254 Review.
-
The HERG K+ channel: progress in understanding the molecular basis of its unusual gating kinetics.Eur Biophys J. 2004 Apr;33(2):89-97. doi: 10.1007/s00249-003-0338-3. Epub 2003 Sep 10. Eur Biophys J. 2004. PMID: 13680209 Review.
Cited by
-
Endocytosis of HERG is clathrin-independent and involves arf6.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 31;8(12):e85630. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085630. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24392021 Free PMC article.
-
Digging into Lipid Membrane Permeation for Cardiac Ion Channel Blocker d-Sotalol with All-Atom Simulations.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Feb 1;9:26. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00026. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29449809 Free PMC article.
-
Implications of Human Transient Receptor Potential Melastatin 8 (TRPM8) Channel Gating from Menthol Binding Studies of the Sensing Domain.Biochemistry. 2016 Jan 12;55(1):114-24. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00931. Epub 2015 Dec 23. Biochemistry. 2016. PMID: 26653082 Free PMC article.
-
Allosteric Coupling Between Drug Binding and the Aromatic Cassette in the Pore Domain of the hERG1 Channel: Implications for a State-Dependent Blockade.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Jun 30;11:914. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00914. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32694995 Free PMC article.
-
Sig1R protein regulates hERG channel expression through a post-translational mechanism in leukemic cells.J Biol Chem. 2011 Aug 12;286(32):27947-58. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.226738. Epub 2011 Jun 16. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21680736 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arcangeli A. Expression and role of hERG channels in cancer cells. Novartis Found Symp 266: 225–232, discussion 232–224, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Bai Y, Wang J, Shan H, Lu Y, Zhang Y, Luo X, Yang B, Wang Z. Sphingolipid metabolite ceramide causes metabolic perturbation contributing to HERG K+ channel dysfunction. Cell Physiol Biochem 20: 429–440, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Balijepalli RC, Delisle BP, Balijepalli SY, Foell JD, Slind JK, Kamp TJ, January CT. Kv11.1 (ERG1) K+ channels localize in cholesterol and sphingolipid enriched membranes and are modulated by membrane cholesterol. Channels (Austin) 1: 263–272, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Barbuti A, Gravante B, Riolfo M, Milanesi R, Terragni B, DiFrancesco D. Localization of pacemaker channels in lipid rafts regulates channel kinetics. Circ Res 94: 1325–1331, 2004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

