Time trends in outcome of subarachnoid hemorrhage: Population-based study and systematic review
- PMID: 20375310
- PMCID: PMC2875923
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181dd42b3
Time trends in outcome of subarachnoid hemorrhage: Population-based study and systematic review
Abstract
Background: Treatment of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) has changed substantially over the last 25 years but there is a lack of reliable population-based data on whether case-fatality or functional outcomes have improved.
Methods: We determined changes in the standardized incidence and outcome of SAH in the same population between 1981 and 1986 (Oxford Community Stroke Project) and 2002 and 2008 (Oxford Vascular Study). In a meta-analysis with other population-based studies, we used linear regression to determine time trends in outcome.
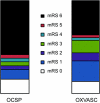
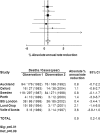
Results: There were no reductions in incidence of SAH (RR = 0.79, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.48-1.29, p = 0.34) and in 30-day case-fatality (RR = 0.67, 95% CI 0.39-1.13, p = 0.14) in the Oxford Vascular Study vs Oxford Community Stroke Project, but there was a decrease in overall mortality (RR = 0.47, 0.23-0.97, p = 0.04). Following adjustment for age and baseline SAH severity, patients surviving to hospital had reduced risk of death or dependency (modified Rankin score > 3) at 12 months in the Oxford Vascular Study (RR = 0.51, 0.29-0.88, p = 0.01). Among 32 studies covering 39 study periods from 1980 to 2005, 7 studied time trends within single populations. Unadjusted case-fatality fell by 0.9% per annum (0.3-1.5, p = 0.007) in a meta-analysis of data from all studies, and by 0.9% per annum (0.2-1.6%, p = 0.01) within the 7 population studies.
Conclusion: Mortality due to subarachnoid hemorrhage fell by about 50% in our study population over the last 2 decades, due mainly to improved outcomes in cases surviving to reach hospital. This improvement is consistent with a significant decrease in case-fatality over the last 25 years in our pooled analysis of other similar population-based studies.
Figures


Comment in
-
Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: have outcomes really improved?Neurology. 2010 May 11;74(19):1486-7. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181e0ef1a. Epub 2010 Apr 21. Neurology. 2010. PMID: 20410463 No abstract available.
References
-
- Nieuwkamp DJ, Setz LE, Algra A, Linn FH, de Rooij NK, Rinkel GJ. Changes in case fatality of aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage over time, according to age, sex, and region: a meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol 2009;8:635–642. - PubMed
-
- Hop JW, Rinkel GJ, Algra A, van Gijn J. Case-fatality rates and functional outcome after subarachnoid hemorrhage: a systematic review. Stroke 1997;28:660–664. - PubMed
-
- Feigin VL, Lawes CM, Bennett DA, Barker-Collo SL, Parag V. Worldwide stroke incidence and early case fatality reported in 56 population-based studies: a systematic review. Lancet Neurol 2009;8:355–369. - PubMed
-
- Wiebers DO, Whisnant JP, Huston J 3rd, et al. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: natural history, clinical outcome, and risks of surgical and endovascular treatment. Lancet 2003;362:103–110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
