Deciphering the structure and function of Als2cr4 in the mouse retina
- PMID: 20375344
- PMCID: PMC2941180
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.10-5251
Deciphering the structure and function of Als2cr4 in the mouse retina
Abstract
Purpose: The role of Als2cr4 (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 2 [juvenile] chromosome region, candidate 4; also known as hypothetical protein FLJ33282) in the mouse retina was determined by characterizing the molecular structure, cellular interacting partners, and potential biochemical functions. Previous in situ hybridization and gene expression profiles show that the mRNAs encoding Als2cr4 are abundant in the eye, hippocampus, cerebellum, and olfactory bulb.
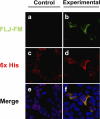
Methods: From predicted antigenic epitopes of Als2cr4, two novel antibodies were developed to examine protein expression and morphologic localization in retinas from light-adapted and dark-adapted mice by immunohistochemistry, immunoblot analysis, and immunoelectron microscopy, and then immunoprecipitation was performed to identify interacting proteins by mass spectroscopy.
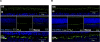
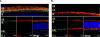
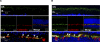
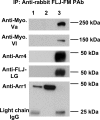
Results: Peptide antibodies with Als2cr4 antigenic epitopes from either the amino- or carboxyl terminus were characterized with Als2cr4 recombinant proteins and peptide competition assays. Als2cr4 is a 45-kDa insoluble protein, highly enriched in retina, and localizes to photoreceptor outer segments, ciliary complex, and horizontal cells in the outer plexiform layer. Immunoelectron microscopy for Als2cr4 verified its expression in the discs of photoreceptor outer segments. Immunoprecipitation and mass spectroscopy identified eight potential interacting partners: vimentin, actin, myosin Va, myosin VI, myosin X, myosin XIV, kinesin 1, Als2cr4, and lamin B-1.
Conclusions: Als2cr4 is a novel protein, with a probable tetraspanin-like membrane structure, that is localized in photoreceptors and in the postsynaptic outer plexiform layer and that interacts with cytoskeletal proteins. Als2cr4 may be involved in membrane transport between the photoreceptor inner and outer segments and may be a key component in maintaining the structural integrity of the outer segment.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Interaction between the photoreceptor-specific tubby-like protein 1 and the neuronal-specific GTPase dynamin-1.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007 Jun;48(6):2837-44. doi: 10.1167/iovs.06-0059. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007. PMID: 17525220 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoschisin is a peripheral membrane protein with affinity for anionic phospholipids and affected by divalent cations.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007 Mar;48(3):991-1000. doi: 10.1167/iovs.06-0915. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007. PMID: 17325137
-
Protein partners of dynamin-1 in the retina.Vis Neurosci. 2013 Jul;30(4):129-39. doi: 10.1017/S0952523813000138. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Vis Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23746204 Free PMC article.
-
TULP1 and TUB Are Required for Specific Localization of PRCD to Photoreceptor Outer Segments.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 17;21(22):8677. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228677. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33213002 Free PMC article.
-
PRCD is concentrated at the base of photoreceptor outer segments and is involved in outer segment disc formation.Hum Mol Genet. 2019 Dec 15;28(24):4078-4088. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddz248. Hum Mol Genet. 2019. PMID: 31628458
Cited by
-
Identification of transmembrane protein 237 as a novel interactor with the intestinal riboflavin transporter-3 (RFVT-3): role in functionality and cell biology.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019 Jun 1;316(6):C805-C814. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00029.2019. Epub 2019 Mar 20. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30892938 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of retinal pigment epithelium cells after exposure to UVA radiation.BMC Ophthalmol. 2019 Aug 2;19(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s12886-019-1151-9. BMC Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 31375076 Free PMC article.
-
HIF-1α-activated TMEM237 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via the NPHP1/Pyk2/ERK pathway.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023 Apr 11;80(5):120. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-04767-y. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37041420 Free PMC article.
-
Visual Cone Arrestin 4 Contributes to Visual Function and Cone Health.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015 Aug;56(9):5407-16. doi: 10.1167/iovs.15-16647. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015. PMID: 26284544 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering missing pieces: duplication and deletion history of arrestins in deuterostomes.BMC Evol Biol. 2017 Jul 6;17(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s12862-017-1001-4. BMC Evol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28683816 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Palczewski K, Saari JC. Activation and inactivation steps in the visual transduction pathway. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1997;7:500–504 - PubMed
-
- Fuchs S, Nakazawa M, Maw M, Tamai M, Oguchi Y, Gal A. A homozygous 1-base pair deletion in the arrestin gene is a frequent cause of Oguchi disease in Japanese. Nat Genet. 1995;10:360–362 - PubMed
-
- Craft CM, Whitmore DH, Wiechmann AF. Cone arrestin identified by targeting expression of a functional family. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:4613–4619 - PubMed
-
- Murakami A, Yajima T, Sakuma H, McLaren MJ, Inana G. X-arrestin: a new retinal arrestin mapping to the X chromosome. FEBS Lett. 1993;334:203–209 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

