Cardiac involvement with parasitic infections
- PMID: 20375355
- PMCID: PMC2863361
- DOI: 10.1128/CMR.00054-09
Cardiac involvement with parasitic infections
Abstract
Parasitic infections previously seen only in developing tropical settings can be currently diagnosed worldwide due to travel and population migration. Some parasites may directly or indirectly affect various anatomical structures of the heart, with infections manifested as myocarditis, pericarditis, pancarditis, or pulmonary hypertension. Thus, it has become quite relevant for clinicians in developed settings to consider parasitic infections in the differential diagnosis of myocardial and pericardial disease anywhere around the globe. Chagas' disease is by far the most important parasitic infection of the heart and one that it is currently considered a global parasitic infection due to the growing migration of populations from areas where these infections are highly endemic to settings where they are not endemic. Current advances in the treatment of African trypanosomiasis offer hope to prevent not only the neurological complications but also the frequently identified cardiac manifestations of this life-threatening parasitic infection. The lack of effective vaccines, optimal chemoprophylaxis, or evidence-based pharmacological therapies to control many of the parasitic diseases of the heart, in particular Chagas' disease, makes this disease one of the most important public health challenges of our time.
Figures
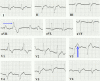
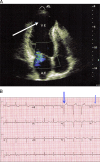
References
-
- Abd-Alla, M. D., T. F. Jackson, V. Gathiram, A. M. el-Hawey, and J. I. Ravdin. 1993. Differentiation of pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica infections from nonpathogenic infections by detection of galactose-inhibitable adherence protein antigen in sera and feces. J. Clin. Microbiol. 31:2845-2850. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Acquatella, H. 2007. Echocardiography in Chagas heart disease. Circulation 115:1124-1131. - PubMed
-
- Adair, O. V., N. Randive, and N. Krasnow. 1989. Isolated toxoplasma myocarditis in acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Am. Heart J. 118:856-857. - PubMed
-
- Adams, J. H., L. Haller, F. Y. Boa, F. Doua, A. Dago, and K. Konian. 1986. Human African trypanosomiasis (T. b. gambiense): a study of 16 fatal cases of sleeping sickness with some observations on acute reactive arsenical encephalopathy. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 12:81-94. - PubMed
-
- Adams, J. L. 1962. Acute toxoplasmosis with involvement of the heart. N. Z. Med. J. 61:20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

