Determination of breast cancer response to bevacizumab therapy using contrast-enhanced ultrasound and artificial neural networks
- PMID: 20375376
- PMCID: PMC3122922
- DOI: 10.7863/jum.2010.29.4.577
Determination of breast cancer response to bevacizumab therapy using contrast-enhanced ultrasound and artificial neural networks
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this study was to evaluate contrast-enhanced ultrasound and neural network data classification for determining the breast cancer response to bevacizumab therapy in a murine model.
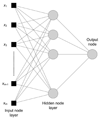
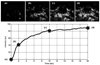
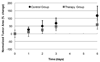
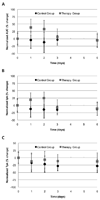
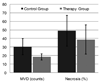
Methods: An ultrasound scanner operating in the harmonic mode was used to measure ultrasound contrast agent (UCA) time-intensity curves in vivo. Twenty-five nude athymic mice with orthotopic breast cancers received a 30-microL tail vein bolus of a perflutren microsphere UCA, and baseline tumor imaging was performed using microbubble destruction-replenishment techniques. Subsequently, 15 animals received a 0.2-mg injection of bevacizumab, whereas 10 control animals received an equivalent dose of saline. Animals were reimaged on days 1, 2, 3, and 6 before euthanasia. Histologic assessment of excised tumor sections was performed. Time-intensity curve analysis for a given region of interest was conducted using customized software. Tumor perfusion metrics on days 1, 2, 3, and 6 were modeled using neural network data classification schemes (60% learning and 40% testing) to predict the breast cancer response to therapy.
Results: The breast cancer response to a single dose of bevacizumab in a murine model was immediate and transient. Permutations of input to the neural network data classification scheme revealed that tumor perfusion data within 3 days of bevacizumab dosing was sufficient to minimize the prediction error to 10%, whereas measurements of physical tumor size alone did not appear adequate to assess the therapeutic response.
Conclusions: Contrast-enhanced ultrasound may be a useful tool for determining the response to bevacizumab therapy and monitoring the subsequent restoration of blood flow to breast cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Relf M, LeJeune S, Scott PAE, et al. Expression of the angiogenic factors vascular endothelial cell growth factor, acidic and basic fibroblast growth factor, tumor growth factor β-1, platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor, placenta growth factor, and pleiotrophin in human primary breast cancer and its relation to angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 1997;57:963–969. - PubMed
-
- Folkman J. How is blood vessel growth regulated in normal and neoplastic tissue? Cancer Res. 1986;46:467–473. - PubMed
-
- Jain RK. Normalizing tumor vasculature with anti-angiogenic therapy: a new paradigm for combination therapy. Nat Med. 2001;7:987–989. - PubMed
-
- Jain RK. Determinants of tumor blow flow: a review. Cancer Res. 1988;48:2641–2658. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

