Natural killer T cells and atherosclerosis: form and function meet pathogenesis
- PMID: 20375560
- PMCID: PMC2895753
- DOI: 10.1159/000296915
Natural killer T cells and atherosclerosis: form and function meet pathogenesis
Abstract
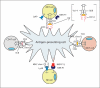
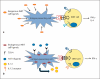
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by dyslipidemia and accumulation of lipids in the arterial intima, with activation of both innate and adaptive immunity. Reciprocally, dyslipidemia associated with atherosclerosis can perturb normal immune function. Natural killer T (NKT) cells are a specialized group of immune cells that share characteristics with both conventional T cells and natural killer cells. However, unlike these cells, NKT cells recognize glycolipid antigens and produce both pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines upon activation. Because of these unique characteristics, NKT cells have recently been ascribed a role in the regulation of immunity and inflammation, including cardiovascular disease. In addition, NKT cells represent a bridge between dyslipidemia and immune regulation. This review summarizes the current knowledge of NKT cells and discusses the interplay between dyslipidemia and the normal functions of NKT cells and how this might modulate inflammation and atherosclerosis.
(c) 2010 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures
References
-
- Epstein SE, Zhu J, Burnett MS, Zhou YF, Vercellotti G, Hajjar D. Infection and atherosclerosis: potential roles of pathogen burden and molecular mimicry. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000;20:1417–1420. - PubMed
-
- Farrugia PM, Lucariello R, Coppola JT. Human immunodeficiency virus and atherosclerosis. Cardiol Rev. 2009;17:211–215. - PubMed
-
- Matsuura E, Kobayashi K, Lopez LR. Atherosclerosis in autoimmune diseases. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2009;11:61–69. - PubMed
-
- Van Oosten M, Rensen PC, Van Amersfoort ES, Van Eck M, Van Dam AM, Breve JJ, Vogel T, Panet A, Van Berkel TJ, Kuiper J. Apolipoprotein E protects against bacterial lipopolysaccharide-induced lethality. A new therapeutic approach to treat gram-negative sepsis. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:8820–8824. - PubMed
-
- Hyka N, Dayer J-M, Modoux C, Kohno T, Edwards CK, Roux-Lombard P, Burger D. Apolipoprotein A-I inhibits the production of interleukin 1b and tumor necrosis factor-α by blocking contact-mediated activation of monocytes by T lymphocytes. Blood. 2001;97:2381–2389. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

