Single-stranded DNA oligoaptamers: molecular recognition and LPS antagonism are length- and secondary structure-dependent
- PMID: 20375565
- PMCID: PMC7312852
- DOI: 10.1159/000145542
Single-stranded DNA oligoaptamers: molecular recognition and LPS antagonism are length- and secondary structure-dependent
Abstract
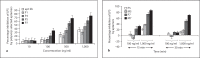
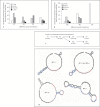
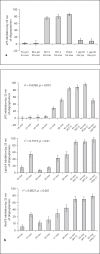
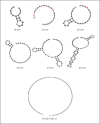
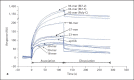
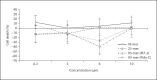
In Gram-negative bacterial infection, lipopolysaccharide (LPS) readily overwhelms the host innate immune system, which could result in inflammation and sepsis in severe cases. Therefore, developing anti-LPS molecules would confer an efficient antibacterial strategy. We used SELEX (Systemic Evolution of Ligands by EXponential enrichment) to isolate single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) aptamers. By immobilizing and exposing different orientations of the LPS molecule on hydrophobic and hydrophilic surfaces, two populations of aptamers were captured from a library of 10(14-15) ssDNA oligonucleotides. Progressive SELEX enriched the aptamers towards thymidine residues. The more hydrophobic aptamers with T-rich loops showed strong molecular recognition for the lipid A moiety of LPS, binding at affinity of up to K(D) of 10(-9)M, and eliciting 95% neutralization of endotoxicity. The longer ssDNAs exhibited greater avidity for LPS and conferred more efficacious antagonism against LPS. The nucleotide composition imposes subtle influence on the aptamer folding and affinity for LPS.
Copyright 2008 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures

References
-
- Downey JS, Han J. Cellular activation mechanisms in septic shock. Front Biosci. 1998;3:d468–d476. - PubMed
-
- Tall A. Plasma lipid transfer proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1995;64:235–257. - PubMed
-
- Brun-Buisson C, Doyon F, Carlet J, Dellamonica P, Gouin F, Lepoutre A, Mercier JC, Offenstadt G, Regnier B. Incidence, risk factors, and outcome of severe sepsis and septic shock in adults. A multicenter prospective study in intensive care units. French ICU Group for Severe Sepsis. JAMA. 1995;274:968–974. - PubMed
-
- Lamping N, Hoess A, Yu B, Park TC, Kirschning CJ, Pfeil D, Reuter D, Wright SD, Herrmann F, Schumann RR. Effects of site-directed mutagenesis of basic residues (Arg 94, Lys 95, Lys 99) of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding protein on binding and transfer of LPS and subsequent immune cell activation. J Immunol. 1996;157:4648–4656. - PubMed
-
- Schumann RR, Leong SR, Flaggs GW, Gray PW, Wright SD, Mathison JC, Tobias PS, Ulevitch RJ. Structure and function of lipopolysaccharide binding protein. Science. 1990;249:1429–1431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

