Toll-like receptor-9 expression is inversely correlated with estrogen receptor status in breast cancer
- PMID: 20375566
- PMCID: PMC7312844
- DOI: 10.1159/000151602
Toll-like receptor-9 expression is inversely correlated with estrogen receptor status in breast cancer
Abstract
Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) recognizes microbial and vertebrate DNA. We previously demonstrated TLR9 expression in human breast cancer cell lines and showed that TLR9 ligands stimulate their in vitro invasion. The aim of this study was to characterize TLR9 expression in clinical breast cancer specimens. Immunohistochemical staining intensity was compared with known baseline prognostic factors and distant metastasis-free survival. TLR9 expression was detected in 98% of the tumors studied (n = 141). The mean TLR9 staining intensity was higher in ER- than in the highly ER+ breast cancers (p = 0.039). High-grade tumors had significantly increased TLR9 expression (p = 0.027) compared with lower-grade tumors. The highest TLR9 expression was detected in the mucinous and the lowest in the tubular breast cancers (p = 0.034). Distant metastasis-free survival was higher in the lower TLR9-expressing half of the cohort than in the higher TLR9-expressing group (p = 0.118). TLR9 expression did not correlate with menopausal, PgR or Her2 status, patient age, tumor proliferative or invasive characteristics.
Copyright 2008 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures

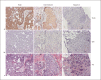
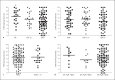
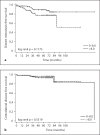
Similar articles
-
Estrogen receptor-α and sex steroid hormones regulate Toll-like receptor-9 expression and invasive function in human breast cancer cells.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012 Apr;132(2):411-9. doi: 10.1007/s10549-011-1590-3. Epub 2011 May 24. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012. PMID: 21607583
-
Toll-like receptor 9 expression in breast and ovarian cancer is associated with poorly differentiated tumors.Cancer Sci. 2010 Apr;101(4):1059-66. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01491.x. Epub 2010 Jan 12. Cancer Sci. 2010. PMID: 20156214 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of toll-like receptor-9 is increased in poorly differentiated prostate tumors.Prostate. 2010 Jun 1;70(8):817-24. doi: 10.1002/pros.21115. Prostate. 2010. PMID: 20054821
-
Toll-like receptor 9 in breast cancer.Front Immunol. 2014 Jul 22;5:330. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00330. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25101078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding the Role of Toll-Like Receptors 9 in Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jul 27;16(15):2679. doi: 10.3390/cancers16152679. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39123407 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Human papillomavirus E6 alters Toll-like receptor 9 transcripts and chemotherapy responses in breast cancer cells in vitro.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Dec 7;52(1):43. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-10143-1. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39644451 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory Response Genes' Polymorphism Associated with Risk of Rheumatic Heart Disease.J Pers Med. 2024 Jul 15;14(7):753. doi: 10.3390/jpm14070753. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 39064007 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in the response to viral infections: TLR8 and TLR9 ligand stimulation induce higher IL10 production in males.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39853. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039853. Epub 2012 Jun 29. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22768144 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor infiltrating CD8+ T lymphocyte count is independent of tumor TLR9 status in treatment naïve triple negative breast cancer and renal cell carcinoma.Oncoimmunology. 2015 May 22;4(6):e1002726. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2014.1002726. eCollection 2015 Jun. Oncoimmunology. 2015. PMID: 26155410 Free PMC article.
-
Gender-specific associations between polymorphisms in the Toll-like receptor (TLR) genes and lung function among workers in swine operations.J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2018;81(22):1186-1198. doi: 10.1080/15287394.2018.1544523. Epub 2018 Nov 12. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2018. PMID: 30418797 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akira S, Hemmi H. Recognition of pathogen-associated molecular patterns by TLR family. Immunol Lett. 2003;85:85–95. - PubMed
-
- Wagner H. The immunobiology of the TLR9 subfamily. Trends Immunol. 2004;25:381–386. - PubMed
-
- Marshak-Rothstein A, Rifkin IR. Immunologically active autoantigens: the role of toll-like receptors in the development of chronic inflammatory disease. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:419–441. - PubMed
-
- Matsumoto M, Funami K, Tanabe M, Oshiumi H, Shingai M, Seto Y, Yamamoto A, Seya T. Subcellular localization of Toll-like receptor 3 in human dendritic cells. J Immunol. 2003;71:3154–3162. - PubMed
-
- Nishiya T, DeFranco AL. Ligand-regulated chimeric receptor approach reveals distinctive subcellular localization and signaling properties of the Toll-like receptors. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:19008–19017. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

