SR-A, MARCO and TLRs differentially recognise selected surface proteins from Neisseria meningitidis: an example of fine specificity in microbial ligand recognition by innate immune receptors
- PMID: 20375573
- PMCID: PMC7312862
- DOI: 10.1159/000155227
SR-A, MARCO and TLRs differentially recognise selected surface proteins from Neisseria meningitidis: an example of fine specificity in microbial ligand recognition by innate immune receptors
Abstract
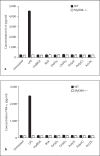
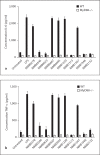
Macrophages express various classes of pattern recognition receptors involved in innate immune recognition of artificial, microbial and host-derived ligands. These include the scavenger receptors (SRs), which are important for phagocytosis, and the Toll-like receptors (TLRs) involved in microbe sensing. The class A macrophage scavenger receptor (SR-A) and macrophage receptor with a collagenous structure (MARCO) display similar domain structures and ligand-binding specificity, which has led to the assumption that these two receptors may be functionally redundant. In this study we show that SR-A and MARCO differentially recognise artificial polyanionic ligands as well as surface proteins from the pathogenic bacterium Neisseria meningitidis. We show that, while acetylated low-density lipoprotein (AcLDL) is a strong ligand for SR-A, it is not a ligand for MARCO. Of the neisserial proteins that were SR ligands, some were ligands for both receptors, while other proteins were only recognised by either SR-A or MARCO. We also analysed the potential of these ligands to act as TLR agonists and assessed the requirement for SR-A and MARCO in pro-inflammatory cytokine induction. SR ligation alone did not induce cytokine production; however, for proteins that were both SR and TLR ligands, the SRs were required for full activation of TLR pathways.
Copyright 2008 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures



References
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;124:783–801. - PubMed
-
- Gordon S. Pattern recognition receptors: doubling up for the innate immune response. Cell. 2002;111:927–930. - PubMed
-
- Taylor PR, Martinez-Pomares L, Stacey M, Lin H-H, Brown GD, Gordon S. Macrophage receptors and immune recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:901–944. - PubMed
-
- O'Neill LA. How Toll-like receptors signal: what we know and what we don't know. Curr Opin Immunol. 2006;18:3–9. - PubMed
-
- Krieger M. The other side of scavenger receptors: pattern recognition for host defense. Curr Opin Lipidol. 1997;8:275–280. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

