Mouse neutrophil extracellular traps in microbial infections
- PMID: 20375576
- PMCID: PMC6951040
- DOI: 10.1159/000205281
Mouse neutrophil extracellular traps in microbial infections
Abstract
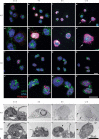
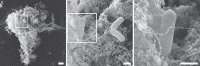
Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) play an important role in innate immunity to microbial infections. NETs have been described in several species, but the molecular details of NET formation and their role in infection has not been addressed, partly because we lack optimal experimental models. Here we describe tools to investigate NET formation in neutrophils isolated from mice. Upon in vitro stimulation of wild-type mouse neutrophils with PMA, we analyzed 3 important steps in the process of NET formation: reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, NET cell death and NET release. As expected, neutrophils from NADPH oxidase-deficient mice failed to produce ROS and did not die nor release NETs upon stimulation. We found that neutrophils from several mouse strains produced NETs with different efficiency and that NET formation correlated with the amount of ROS produced. Activation with Candida albicans also resulted in ROS production and NET cell death. The hyphal form of this fungus induced NETs more effectively than the yeast form. With this work, we provide tools to study in vitro NET assembly in the mouse system.
Copyright 2009 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Rab27a is essential for the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) in neutrophil-like differentiated HL60 cells.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 3;9(1):e84704. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084704. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24404184 Free PMC article.
-
The atypical small GTPase GEM/Kir is a negative regulator of the NADPH oxidase and NETs production through macroautophagy.J Leukoc Biol. 2021 Oct;110(4):629-649. doi: 10.1002/JLB.2HI0421-123R. Epub 2021 Jun 4. J Leukoc Biol. 2021. PMID: 34085299
-
Killing by neutrophil extracellular traps: fact or folklore?Blood. 2012 Feb 2;119(5):1214-6. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-07-364604. Epub 2011 Dec 30. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22210873
-
Neutrophil extracellular traps: a strategic tactic to defeat pathogens with potential consequences for the host.J Innate Immun. 2009;1(3):176-80. doi: 10.1159/000203699. Epub 2009 Feb 20. J Innate Immun. 2009. PMID: 20375575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Candida albicans Infection.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 16;13:913028. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.913028. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35784323 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prolonged exposure to neutrophil extracellular traps can induce mitochondrial damage in macrophages and dendritic cells.Springerplus. 2015 Apr 2;4:161. doi: 10.1186/s40064-015-0932-8. eCollection 2015. Springerplus. 2015. PMID: 25883887 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophils from Both Susceptible and Resistant Mice Efficiently Kill Opsonized Listeria monocytogenes.Infect Immun. 2018 Mar 22;86(4):e00085-18. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00085-18. Print 2018 Apr. Infect Immun. 2018. PMID: 29426040 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil extracellular traps: from physiology to pathology.Cardiovasc Res. 2022 Oct 21;118(13):2737-2753. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvab329. Cardiovasc Res. 2022. PMID: 34648022 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions between polymorphonuclear leukocytes and Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms on silicone implants in vivo.Infect Immun. 2012 Aug;80(8):2601-7. doi: 10.1128/IAI.06215-11. Epub 2012 May 14. Infect Immun. 2012. PMID: 22585963 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation Is Independent of De Novo Gene Expression.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 16;11(6):e0157454. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157454. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27310721 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nathan C. Neutrophils and immunity: challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev. 2006;6:173–182. - PubMed
-
- Faurschou M, Borregaard N. Neutrophil granules and secretory vesicles in inflammation. Microbes Infect. 2003;5:1317–1327. - PubMed
-
- Brinkmann V, Reichard U, Goosmann C, Fauler B, Uhlemann Y, Weiss DS, Weinrauch Y, Zychlinsky A. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science. 2004;303:1532–1535. - PubMed
-
- Alghamdi AS, Foster DN. Seminal DNase frees spermatozoa entangled in neutrophil extracellular traps. Biol Reprod. 2005;73:1174–1181. - PubMed
-
- Lippolis JD, Reinhardt TA, Goff JP, Horst RL. Neutrophil extracellular trap formation by bovine neutrophils is not inhibited by milk. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2006;113:248–255. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

