The complete mitochondrial genome of the fall webworm, Hyphantria cunea (Lepidoptera: Arctiidae)
- PMID: 20376208
- PMCID: PMC2850540
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.6.172
The complete mitochondrial genome of the fall webworm, Hyphantria cunea (Lepidoptera: Arctiidae)
Abstract
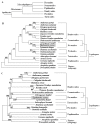
The complete mitochondrial genome (mitogenome) of the fall webworm, Hyphantria cunea (Lepidoptera: Arctiidae) was determined. The genome is a circular molecule 15 481 bp long. It presents a typical gene organization and order for completely sequenced lepidopteran mitogenomes, but differs from the insect ancestral type for the placement of tRNA(Met). The nucleotide composition of the genome is also highly A + T biased, accounting for 80.38%, with a slightly positive AT skewness (0.010), indicating the occurrence of more As than Ts, as found in the Noctuoidea species. All protein-coding genes (PCGs) are initiated by ATN codons, except for COI, which is tentatively designated by the CGA codon as observed in other lepidopterans. Four of 13 PCGs harbor the incomplete termination codon, T or TA. All tRNAs have a typical clover-leaf structure of mitochondrial tRNAs, except for tRNA(Ser)(AGN), the DHU arm of which could not form a stable stem-loop structure. The intergenic spacer sequence between tRNA(Ser)(AGN) and ND1 also contains the ATACTAA motif, which is conserved across the Lepidoptera order. The H. cunea A+T-rich region of 357 bp is comprised of non-repetitive sequences, but harbors several features common to the Lepidoptera insects, including the motif ATAGA followed by an 18 bp poly-T stretch, a microsatellite-like (AT)(8) element preceded by the ATTTA motif, an 11 bp poly-A present immediately upstream tRNA(Met). The phylogenetic analyses support the view that the H. cunea is closerly related to the Lymantria dispar than Ochrogaster lunifer, and support the hypothesis that Noctuoidea (H. cunea, L. dispar, and O. lunifer) and Geometroidea (Phthonandria atrilineata) are monophyletic. However, in the phylogenetic trees based on mitogenome sequences among the lepidopteran superfamilies, Papillonoidea (Artogeia melete, Acraea issoria, and Coreana raphaelis) joined basally within the monophyly of Lepidoptera, which is different to the traditional classification.
Keywords: Arctiidae; Fall webworm; Hyphantria cunea; Lepidoptera; Mitochondrial genome; Phylogeny.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The complete mitochondrial genome of the Ailanthus silkmoth, Samia cynthia cynthia (Lepidoptera: Saturniidae).Gene. 2013 Sep 10;526(2):309-17. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.05.048. Epub 2013 Jun 5. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23747351
-
The complete nucleotide sequence of the mitochondrial genome of the cabbage butterfly, Artogeia melete (Lepidoptera: Pieridae).Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2009 Jun;41(6):446-55. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmp030. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2009. PMID: 19499147
-
Complete mitochondrial genome of the laced fritillary Argyreus hyperbius (Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae).Dongwuxue Yanjiu. 2011 Oct;32(5):465-75. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1141.2011.05465. Dongwuxue Yanjiu. 2011. PMID: 22006797
-
Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome of Biston marginata (Lepidoptera: Geometridae) and phylogenetic analysis among lepidopteran insects.Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 Jul 1;113:961-970. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.02.110. Epub 2018 Feb 17. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018. PMID: 29462677
-
Characterization of the Complete Mitochondrial Genome of Leucoma salicis (Lepidoptera: Lymantriidae) and Comparison with Other Lepidopteran Insects.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 15;6:39153. doi: 10.1038/srep39153. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27974854 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The complete mitochondrial genome of the rice moth, Corcyra cephalonica.J Insect Sci. 2012;12:72. doi: 10.1673/031.012.7201. J Insect Sci. 2012. PMID: 23413968 Free PMC article.
-
The complete mitochondrial genome of the Chinese Daphnia pulex (Cladocera, Daphniidae).Zookeys. 2016 Sep 7;(615):47-60. doi: 10.3897/zookeys.615.8581. eCollection 2016. Zookeys. 2016. PMID: 27667940 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenetic analysis of the complete mitochondrial genome of the Blomfild's Beauty butterfly Smyrna blomfildia (Fabricius 1781) (Insecta: Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae: Nymphalini).Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2021 Oct 14;6(11):3199-3201. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2021.1989337. eCollection 2021. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2021. PMID: 34660902 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative mitochondrial genome analysis of Daphnis nerii and other lepidopteran insects reveals conserved mitochondrial genome organization and phylogenetic relationships.PLoS One. 2017 Jun 9;12(6):e0178773. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178773. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28598968 Free PMC article.
-
Host and phenology shifts in the evolution of the social moth genus Thaumetopoea.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57192. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057192. Epub 2013 Feb 27. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23460830 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Warren LO, Tadic M. The fall webworm, Hyphantria cunea (Drury) Ark Agric Exp Stn Bull. 1970;759:1–106.
-
- Umeya K, Itô Y. Hidaka T (ed) Adaptation and speciation in the fall webworm. Kodansha, Tokyo; 1977. Invasion and establishment of a new insect pest in Japan.
-
- Ji R, Xie BY, Li XH. et al.Research progress on the invasive species, Hyphantria cunea. Entomol Knowledge (China) 2003;40:13–18.
-
- Wolstenholme DR. Animal mitochondrial DNA: Structure and evolution. Int Rev Cytol. 1992;141:173–216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

