Gas-phase rearrangements do not affect site localization reliability in phosphoproteomics data sets
- PMID: 20377248
- PMCID: PMC2912977
- DOI: 10.1021/pr1000225
Gas-phase rearrangements do not affect site localization reliability in phosphoproteomics data sets
Abstract
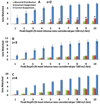
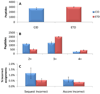
Intramolecular transfer of phosphate during collision-induced dissociation (CID) in ion-trap mass spectrometers has recently been described. Because phosphorylation events are assigned to discrete serine, threonine, and tyrosine residues based on the presence of site-determining ions in MS/MS spectra, phosphate transfer may invalidate or confound site localization in published large-scale phosphorylation data sets. Here, we present evidence for the occurrence of this phenomenon using synthetic phosphopeptide libraries, specifically for doubly charged species. We found, however, that the extent of the transfer reaction was insufficient to cause localization of phosphorylation sites to incorrect residues. We further compared CID to electron-transfer dissociation (ETD) for site localization using synthetic libraries and a large-scale yeast phosphoproteome experiment. The agreement in site localization was >99.5 and 93%, respectively, suggesting that ETD-based site localization is no more reliable than CID. We conclude that intramolecular phosphate transfer does not affect the reliability of current or past phosphorylation data sets.
Figures

References
-
- Palumbo AM, Reid GE. Evaluation of gas-phase rearrangement and competing fragmentation reactions on protein phosphorylation site assignment using collision induced dissociation-MS/MS and MS3. Anal Chem. 2008;80(24):9735. - PubMed
-
- Abu-Farha M, et al. Proteomics: from technology developments to biological applications. Anal Chem. 2009;81(12):4585. - PubMed
-
- Boersema PJ, Mohammed S, Heck AJ. Phosphopeptide fragmentation and analysis by mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrom. 2009;44(6):861. - PubMed
-
- Edelson-Averbukh M, Shevchenko A, Pipkorn R, Lehmann WD. Gas-phase intramolecular phosphate shift in phosphotyrosine-containing peptide monoanions. Anal Chem. 2009;81(11):4369. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

