Host-cell lipid rafts: a safe door for micro-organisms?
- PMID: 20377525
- PMCID: PMC7161784
- DOI: 10.1042/BC20090138
Host-cell lipid rafts: a safe door for micro-organisms?
Abstract
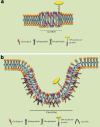
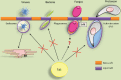
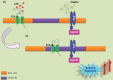
The lipid raft hypothesis proposed that these microdomains are small (10-200 nM), highly dynamic and enriched in cholesterol, glycosphingolipids and signalling phospholipids, which compartmentalize cellular processes. These membrane regions play crucial roles in signal transduction, phagocytosis and secretion, as well as pathogen adhesion/interaction. Throughout evolution, many pathogens have developed mechanisms to escape from the host immune system, some of which are based on the host membrane microdomain machinery. Thus lipid rafts might be exploited by pathogens as signalling and entry platforms. In this review, we summarize the role of lipid rafts as players in the overall invasion process used by different pathogens to escape from the host immune system.
Figures
References
-
- Alexander J. Russell D.G. The interaction of Leishmania species with macrophages Adv. Parasitol. 1992. 31 175–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

