Consequential late effects after radiotherapy for prostate cancer - a prospective longitudinal quality of life study
- PMID: 20377874
- PMCID: PMC2857853
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-5-27
Consequential late effects after radiotherapy for prostate cancer - a prospective longitudinal quality of life study
Abstract
Background: To answer the question if and to which extent acute symptoms at the end and/or several weeks after radiotherapy can predict adverse urinary and gastrointestinal long-term quality of life (QoL).
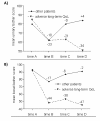
Methods: A group of 298 patients has been surveyed prospectively before (time A), at the last day (B), two months after (C) and >one year after (D) radiotherapy using a validated questionnaire (Expanded Prostate Cancer Index Composite). A subgroup of 10% with the greatest urinary/bowel bother score decrease at time D was defined as patients with adverse long-term QoL.
Results: Subgroup and correlation analyses could demonstrate a strong dependence of urinary/bowel QoL after radiotherapy on urinary/bowel QoL before radiotherapy. In contrast to absolute scores, QoL score changes (relative to baseline scores) did not correlate with pretreatment scores. Long-term changes could be well predicted by acute changes. Patients reporting great/moderate bother with urinary/bowel problems at time C reported to have great/moderate bother at time D in > or = 50%, respectively. In a multivariate analysis of factors for adverse long-term urinary and bowel QoL, score changes at time C were found to be independent predictors, respectively. Additionally, QoL changes at time B were independently predictive for adverse long-term bowel QoL.
Conclusions: Consequential late effects play a major role after radiotherapy for prostate cancer. Patients with greater and particularly longer non-healing acute toxicity are candidates for closer follow-up and possible prophylactic actions to reduce a high probability of long-term problems.
Figures

References
-
- Zapatero A, Garcia-Vicente F, Modolell I, Alcantara P, Floriano A, Cruz-Conde A, Torres JJ, Pérez-Torrubia A. Impact of mean rectal dose on late rectal bleeding after conformal radiotherapy for prostate cancer: dose-volume effect. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004;59:1343–1351. - PubMed
-
- Pinkawa M, Fischedick K, Asadpour B, Gagel B, Piroth MD, Eble MJ. Low-grade toxicity after conformal radiation therapy for prostate cancer - impact of bladder volume. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;64:835–841. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

