N4ITK: improved N3 bias correction
- PMID: 20378467
- PMCID: PMC3071855
- DOI: 10.1109/TMI.2010.2046908
N4ITK: improved N3 bias correction
Abstract
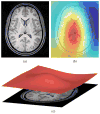
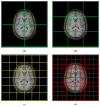
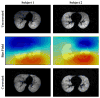
A variant of the popular nonparametric nonuniform intensity normalization (N3) algorithm is proposed for bias field correction. Given the superb performance of N3 and its public availability, it has been the subject of several evaluation studies. These studies have demonstrated the importance of certain parameters associated with the B-spline least-squares fitting. We propose the substitution of a recently developed fast and robust B-spline approximation routine and a modified hierarchical optimization scheme for improved bias field correction over the original N3 algorithm. Similar to the N3 algorithm, we also make the source code, testing, and technical documentation of our contribution, which we denote as "N4ITK," available to the public through the Insight Toolkit of the National Institutes of Health. Performance assessment is demonstrated using simulated data from the publicly available Brainweb database, hyperpolarized (3)He lung image data, and 9.4T postmortem hippocampus data.
Figures



References
-
- Belaroussi B, Milles J, Carme S, Zhu YM, Benoit-Cattin H. Intensity nonuniformity correction in MRI: Existing methods and their validation. Med Image Anal. 2006 Apr;10(2):234–246. - PubMed
-
- Vovk U, Pernus F, Likar B. A review of methods for correction of intensity inhomogeneity in MRI. IEEE Trans Med Imag. 2007 Mar;26(3):405–421. - PubMed
-
- Sled JG, Zijdenbos AP, Evans AC. A nonparametric method for automatic correction of intensity nonuniformity in MRI data. IEEE Trans Med Imag. 1998 Feb;17(1):87–97. - PubMed
-
- Arnold JB, Liow JS, Schaper KA, Stern JJ, Sled JG, Shattuck DW, Worth AJ, Cohen MS, Leahy RM, Mazziotta JC, Rottenberg A. Qualitative and quantitative evaluation of six algorithms for correcting intensity nonuniformity effects. Neuroimage. 2001 May;13(5):931–943. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

