Properties of the TRPML3 channel pore and its stable expansion by the Varitint-Waddler-causing mutation
- PMID: 20378547
- PMCID: PMC2878031
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.078204
Properties of the TRPML3 channel pore and its stable expansion by the Varitint-Waddler-causing mutation
Abstract
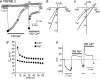
TRPML3 is a H(+)-regulated Ca(2+) channel that shuttles between intracellular compartments and the plasma membrane. The A419P mutation causes the varitint-waddler phenotype as a result of gain-of-function (GOF). The mechanism by which A419P leads to GOF is not known. Here, we show that the TRPML3 pore is dynamic when conducting Ca(2+) to change its conductance and permeability, which appears to be mediated by trapping Ca(2+) within the pore. The pore properties can be restored by strong depolarization or by conducting Na(+) through the pore. The A419P mutation results in expanded channel pore with altered permeability that limits modulation of the pore by Ca(2+). This effect is specific for the A419P mutation and is not reproduced by other GOF mutations, including A419G, H283A, and proline mutations in the fifth transmembrane domain. These findings describe a novel mode of a transient receptor potential channel behavior and suggest that pore expansion by the A419P mutation may contribute to the varitint-waddler phenotype.
Figures




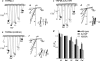

Similar articles
-
A novel mode of TRPML3 regulation by extracytosolic pH absent in the varitint-waddler phenotype.EMBO J. 2008 Apr 23;27(8):1197-205. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2008.56. Epub 2008 Mar 27. EMBO J. 2008. PMID: 18369318 Free PMC article.
-
Gain-of-function mutation in TRPML3 causes the mouse Varitint-Waddler phenotype.J Biol Chem. 2007 Dec 14;282(50):36138-42. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C700190200. Epub 2007 Oct 25. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17962195
-
The varitint-waddler mouse phenotypes and the TRPML3 ion channel mutation: cause and consequence.Pflugers Arch. 2008 Nov;457(2):463-73. doi: 10.1007/s00424-008-0523-4. Epub 2008 May 27. Pflugers Arch. 2008. PMID: 18504603 Review.
-
The varitint-waddler (Va) deafness mutation in TRPML3 generates constitutive, inward rectifying currents and causes cell degeneration.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Jan 8;105(1):353-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0707963105. Epub 2007 Dec 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18162548 Free PMC article.
-
TRPML3 and hearing loss in the varitint-waddler mouse.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Aug;1772(8):1028-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2007.01.007. Epub 2007 Jan 23. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17329082 Review.
Cited by
-
The intracellular Ca²⁺ channels of membrane traffic.Channels (Austin). 2012 Sep-Oct;6(5):344-51. doi: 10.4161/chan.21723. Epub 2012 Aug 21. Channels (Austin). 2012. PMID: 22907062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mucolipin-2 (TRPML2) ion channel: a tissue-specific protein crucial to normal cell function.Pflugers Arch. 2016 Feb;468(2):177-92. doi: 10.1007/s00424-015-1732-2. Epub 2015 Sep 4. Pflugers Arch. 2016. PMID: 26336837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The intracellular Ca2+ channel TRPML3 is a PI3P effector that regulates autophagosome biogenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Oct 25;119(43):e2200085119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2200085119. Epub 2022 Oct 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36252030 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutive activity of TRP channels methods for measuring the activity and its outcome.Methods Enzymol. 2010;484:591-612. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-381298-8.00029-0. Methods Enzymol. 2010. PMID: 21036252 Free PMC article.
-
Cryo-electron microscopy structure of the lysosomal calcium-permeable channel TRPML3.Nature. 2017 Oct 19;550(7676):411-414. doi: 10.1038/nature24055. Epub 2017 Oct 11. Nature. 2017. PMID: 29019979 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nilius B., Owsianik G., Voets T., Peters J. A. (2007) Physiol. Rev. 87, 165–217 - PubMed
-
- Bargal R., Avidan N., Ben-Asher E., Olender Z., Zeigler M., Frumkin A., Raas-Rothschild A., Glusman G., Lancet D., Bach G. (2000) Nat. Genet. 26, 118–123 - PubMed
-
- Atiba-Davies M., Noben-Trauth K. (2007) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1772, 1028–1031 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

