Metabolite profiling identifies markers of uremia
- PMID: 20378825
- PMCID: PMC2900954
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2009111132
Metabolite profiling identifies markers of uremia
Abstract
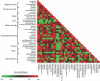
ESRD is a state of small-molecule disarray. We applied liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry-based metabolite profiling to survey>350 small molecules in 44 fasting subjects with ESRD, before and after hemodialysis, and in 10 age-matched, at-risk fasting control subjects. At baseline, increased levels of polar analytes and decreased levels of lipid analytes characterized uremic plasma. In addition to confirming the elevation of numerous previously identified uremic toxins, we identified several additional markers of ESRD, including dicarboxylic acids (adipate, malonate, methylmalonate, and maleate), biogenic amines, nucleotide derivatives, phenols, and sphingomyelins. The pattern of lipids was notable for a universal decrease in lower-molecular-weight triacylglycerols, and an increase in several intermediate-molecular-weight triacylglycerols in ESRD compared with controls; standard measurement of total triglycerides obscured this heterogeneity. These observations suggest disturbed triglyceride catabolism and/or beta-oxidation in ESRD. As expected, the hemodialysis procedure was associated with significant decreases in most polar analytes. Unexpected increases in several metabolites, however, indicated activation of a broad catabolic program, including glycolysis, lipolysis, ketosis, and nucleotide breakdown. In summary, this study demonstrates the application of metabolite profiling to identify markers of ESRD, provide perspective on uremic dyslipidemia, and broaden our understanding of the biochemical effects of hemodialysis.
Figures



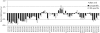
References
-
- Nicholson JK, Wilson ID: Opinion: understanding “global” systems biology: Metabonomics and the continuum of metabolism. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2: 668–676, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Want EJ, Nordstrom A, Morita H, Siuzdak G: From exogenous to endogenous: The inevitable imprint of mass spectrometry in metabolomics. J Proteome Res 6: 459–468, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Newgard CB, An J, Bain JR, Muehlbauer MJ, Stevens RD, Lien LF, Ha AM, Shah SH, Arlotto M, Slentz CA, Rochon J, Gallup D, Ilkayeva O, Wenner BR, Yancy WS, Jr, Eisenson H, Musante G, Surwit RS, Millington DS, Butler MD, Svetkey LP: A branched-chain amino acid-related metabolic signature that differentiates obese and lean humans and contributes to insulin resistance. Cell Metab 9: 311–326, 2009. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

