Pharmacokinetics of 2 novel formulations of modified-release oral testosterone alone and with finasteride in normal men with experimental hypogonadism
- PMID: 20378927
- PMCID: PMC3047498
- DOI: 10.2164/jandrol.109.009746
Pharmacokinetics of 2 novel formulations of modified-release oral testosterone alone and with finasteride in normal men with experimental hypogonadism
Abstract
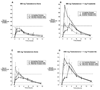
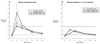
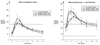
Oral administration of testosterone might be useful for the treatment of testosterone deficiency. However, current "immediate-release" formulations of oral testosterone exhibit suboptimal pharmacokinetics, with supraphysiologic peaks of testosterone and its metabolite, dihydrotestosterone (DHT), immediately after dosing. To dampen these peaks, we have developed 2 novel modified-release formulations of oral testosterone designed to slow absorption from the gut and improve hormone delivery. We studied these testosterone formulations in 16 normal young men enrolled in a 2-arm, open-label clinical trial. Three hundred-mg and 600-mg doses of immediate-release and modified fast-release or slow-release formulations were administered sequentially to 8 normal men rendered hypogonadal by the administration of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist acyline. Blood for measurement of serum testosterone, DHT, and estradiol was obtained before and 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, and 24 hours after each dose. A second group of 8 men was studied with the coadministration of 1 mg of the 5α-reductase inhibitor finasteride daily throughout the treatment period. Serum testosterone was increased with all formulations of oral testosterone. The modified slow-release formulation significantly delayed the postdose peaks of serum testosterone and reduced peak concentrations of serum DHT compared with the immediate-release formulation. The addition of finasteride further increased serum testosterone and decreased serum DHT. We conclude that the oral modified slow-release testosterone formulation exhibits superior pharmacokinetics compared with immediate-release oral testosterone both alone and in combination with finasteride. This formulation might have efficacy for the treatment of testosterone deficiency.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00663793.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pharmacokinetics of modified slow-release oral testosterone over 9 days in normal men with experimental hypogonadism.J Androl. 2012 May-Jun;33(3):420-6. doi: 10.2164/jandrol.111.014514. Epub 2011 Aug 25. J Androl. 2012. PMID: 21868746 Free PMC article.
-
Steady-state pharmacokinetics of oral testosterone undecanoate with concomitant inhibition of 5α-reductase by finasteride.Int J Androl. 2011 Dec;34(6 Pt 1):541-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2605.2010.01120.x. Epub 2010 Oct 24. Int J Androl. 2011. PMID: 20969601 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Oral testosterone in oil: pharmacokinetic effects of 5alpha reduction by finasteride or dutasteride and food intake in men.J Androl. 2006 Jan-Feb;27(1):72-8. doi: 10.2164/jandrol.05058. J Androl. 2006. PMID: 16400081
-
Negative Impact of Testosterone Deficiency and 5α-Reductase Inhibitors Therapy on Metabolic and Sexual Function in Men.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1043:473-526. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-70178-3_22. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 29224108 Review.
-
Dihydrotestosterone and the concept of 5alpha-reductase inhibition in human benign prostatic hyperplasia.Eur Urol. 2000 Apr;37(4):367-80. doi: 10.1159/000020181. Eur Urol. 2000. PMID: 10765065 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacokinetics of modified slow-release oral testosterone over 9 days in normal men with experimental hypogonadism.J Androl. 2012 May-Jun;33(3):420-6. doi: 10.2164/jandrol.111.014514. Epub 2011 Aug 25. J Androl. 2012. PMID: 21868746 Free PMC article.
-
An oral lipidic native testosterone formulation that is absorbed independent of food.Eur J Endocrinol. 2021 Oct 5;185(5):607-615. doi: 10.1530/EJE-21-0606. Eur J Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 34379604 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amory JK, Bremner WJ. Oral testosterone in oil plus dutasteride: a pharmacokinetic study in men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:2610–2617. - PubMed
-
- Amory JK, Page ST, Bremner WJ. Oral testosterone in oil: pharmacokinetic effects of 5α-reduction with finasteride or dutasteride and food intake in men. J Androl. 2006;27:72–78. - PubMed
-
- Amory JK, Wang C, Swerdloff RS, Anawalt BD, Matsumoto AM, Bremner WJ, Walker SE, Haberer LJ, Clark RV. The effect of 5alpha-reductase inhibition with dutasteride and finasteride on semen parameters and serum hormones in healthy men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:1659–1665. - PubMed
-
- Araujo AB, Esche GR, Kupelian V, O’Donnell AB, Travison TG, Williams RE, Clark RV, McKinlay JB. Prevalence of symptomatic androgen deficiency in men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:4241–4247. - PubMed
-
- Bagchus WM, Hust R, Maris F, Schnabel PG, Houwing NS. Important effect of food on the bioavailability of oral testosterone undecanoate. Pharmacotherapy. 2003;23:319–325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
