Proton-Resistant Quantum Dots: Stability in Gastrointestinal Fluids and Implications for Oral Delivery of Nanoparticle Agents
- PMID: 20379372
- PMCID: PMC2850447
- DOI: 10.1007/s12274-009-9046-3
Proton-Resistant Quantum Dots: Stability in Gastrointestinal Fluids and Implications for Oral Delivery of Nanoparticle Agents
Abstract
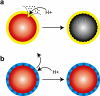
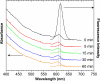
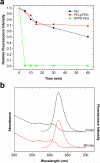
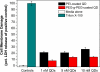
Semiconductor quantum dots (QDs) have shown great promise as fluorescent probes for molecular, cellular and in-vivo imaging. However, the fluorescence of traditional polymer-encapsulated QDs is often quenched by proton-induced etching in acidic environments. This is a major problem for QD applications in the gastrointestinal tract because the gastric (stomach) environment is strongly acidic (pH 1-2). Here we report the use of proton-resistant surface coatings to stabilize QD fluorescence under acidic conditions. Using both hyperbranched polyethylenimine (PEI) and its polyethylene glycol derivative (PEG grafted PEI), we show that the fluorescence of core-shell CdSe/CdS/ZnS QDs is effectively protected from quenching in simulated gastric fluids. In comparison, amphiphilic lipid or polymer coatings provide no protection under similarly acidic conditions. The proton-resistant QDs are found to cause moderate membrane damage to cultured epithelial cells, but PEGylation (PEG grafting) can be used to reduce cellular toxicity and to improved nanoparticle stability.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Biodistribution and stability of CdSe core quantum dots in mouse digestive tract following per os administration: advantages of double polymer/silica coated nanocrystals.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012 Mar 2;419(1):54-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.01.123. Epub 2012 Jan 31. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012. PMID: 22321397
-
Cell-penetrating quantum dots based on multivalent and endosome-disrupting surface coatings.J Am Chem Soc. 2007 Mar 21;129(11):3333-8. doi: 10.1021/ja068158s. Epub 2007 Feb 24. J Am Chem Soc. 2007. PMID: 17319667
-
A systematic examination of surface coatings on the optical and chemical properties of semiconductor quantum dots.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2006 Sep 7;8(33):3895-903. doi: 10.1039/b606572b. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2006. PMID: 19817050
-
64Cu-1,4,7,10-Tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid-quantum dot-vascular endothelial growth factor.2008 Jul 1 [updated 2008 Aug 12]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2008 Jul 1 [updated 2008 Aug 12]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 20641777 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Quantum dot-A10 RNA aptamer-doxorubicin conjugate.2008 Aug 25 [updated 2008 Oct 8]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2008 Aug 25 [updated 2008 Oct 8]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 20641322 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Colloidal stability of polymeric nanoparticles in biological fluids.J Nanopart Res. 2012 Jun;14(6):920. doi: 10.1007/s11051-012-0920-7. Epub 2012 Jun 6. J Nanopart Res. 2012. PMID: 23162376 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticle toxicity by the gastrointestinal route: evidence and knowledge gaps.Int J Biomed Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2013;3(1-2):10.1504/IJBNN.2013.054515. doi: 10.1504/IJBNN.2013.054515. Int J Biomed Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2013. PMID: 24228068 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of UVB exposure and differentiation state of primary keratinocytes on their interaction with quantum dots.Nanotoxicology. 2013 Nov;7(7):1244-54. doi: 10.3109/17435390.2012.733437. Epub 2012 Oct 25. Nanotoxicology. 2013. PMID: 22998293 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial Fabrication of Quantum Dots: Mechanism and Applications.Curr Microbiol. 2024 Aug 2;81(9):294. doi: 10.1007/s00284-024-03813-7. Curr Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39095512 Review.
-
Silica-polymer dual layer-encapsulated quantum dots with remarkable stability.ACS Nano. 2010 Oct 26;4(10):6080-6. doi: 10.1021/nn1017044. ACS Nano. 2010. PMID: 20863118 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alivisatos P. The use of nanocrystals in biological detection. Nat. Biotech. 2004;22:47–52. - PubMed
-
- Gao X, Yang L, Petros JA, Marshall FF, Simons JW, Nie S. In vivo molecular and cellular imaging with quantum dots. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2005;16:63–72. - PubMed
-
- Wu X, Liu H, Liu J, Haley KN, Treadway JA, Larson JP, Ge N, Peale F, Bruchez MP. Immunofluorescent labeling of cancer marker Her2 and other cellular targets with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003;21:41–46. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
